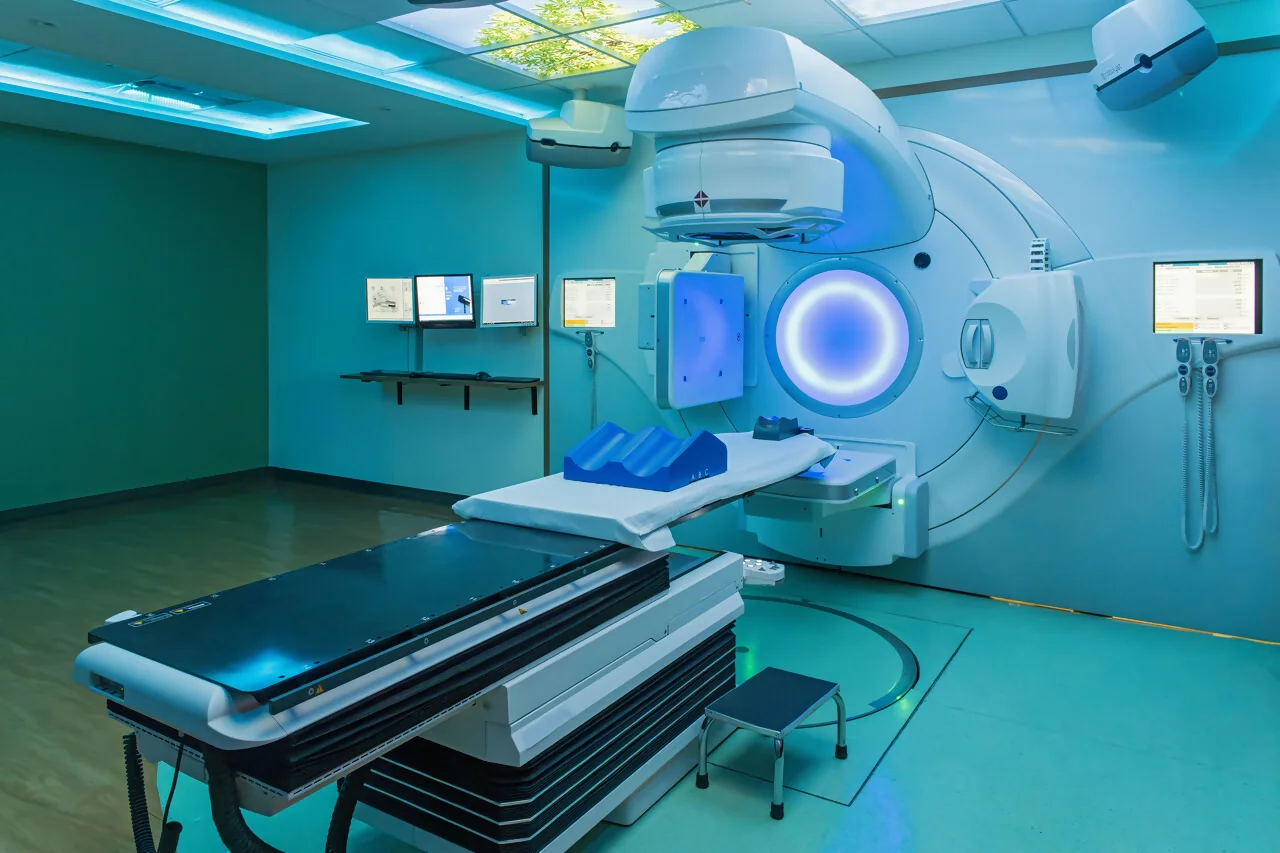
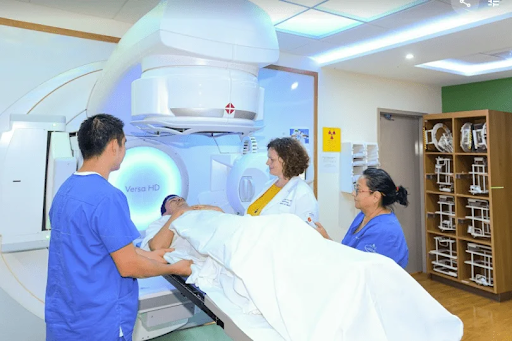
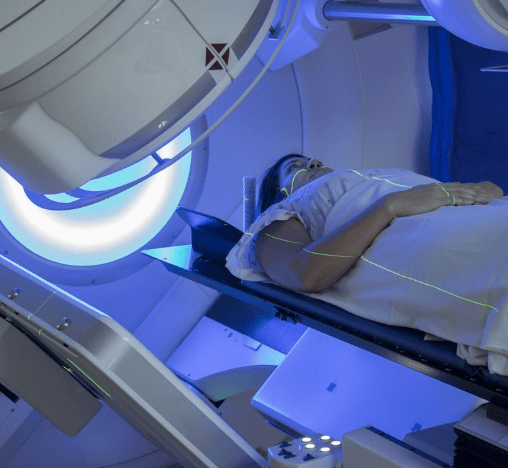
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy plays a fundamental role in the treatment of cancer, being used in up to 70% of cases in advanced centers such as the ABC Cancer Center. The main goal of radiation therapy, like surgery, is to seek local or regional control of the disease.
Our radiation oncologists integrate advanced and sophisticated radiation therapy schemes for the multidisciplinary management of cancer. They design and individualize treatments for a wide range of tumor types and sizes, both primary and metastatic. Highly personalized treatments are performed in adults and children.
Depending on the diagnosis and other specific characteristics of your disease, your radiation oncologist recommends the type of radiotherapy that can benefit you the most. In an early-stage localized tumor, radiotherapy is intended to be curative and may be the only treatment. In combination with surgery, radiation therapy (neoadjuvant) can be used earlier to shrink the tumor, or later (adjuvant) to prevent the cancer from recurring. In advanced metastatic disease, radiation therapy usually has a synergistic effect accompanying chemotherapy and target therapies. Palliative radiation therapy can help control pain or other symptoms caused by metastases.
Why choose our Cancer Center?
- State-of-the-art equipment: We have the latest generation devices and assurance systems to achieve the highest quality and safety standards in all treatment modalities.
- Highly trained staff: Our human team has extensive experience in radiation oncologists, radio-neurosurgeons, medical physicists, dosimetrists, radiation therapy technicians, nursing staff, nursing assistants and administrative staff.
- Ground-breaking technology: We have been the first in Mexico to use specialized intensity-modulated techniques and high-rate brachytherapy with 3D technology.
- International Counseling: From the beginning of its operation, the Radiotherapy Unit has been closely assisted by the Houston Methodist Hospital to generate an exchange of knowledge between both institutions.
- Formative teaching: We are committed to the training of radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and radiation technicians in the country
Get to know our Radiotherapy unit
SRS Certification: Leadership in Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Mexico
Centro Médico ABC has received certification from the International Society for Stereotactic Radiosurgery (ISRS), a recognition that highlights our commitment to excellence in treating patients with intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). This certification establishes us as the only hospital in Mexico and one of just four healthcare centers in Latin America specializing in these advanced technologies. Using electron linear accelerators (8 NOVALIS TX), we achieve submillimeter precision comparable to Gamma Knife, with the added advantage of faster treatment sessions (approximately 60-90 minutes instead of the 2-3 hours required by other devices).

With over 10 years of experience, we provide highly precise treatments for brain tumors, benign conditions, and functional disorders. This certification assures our patients they will receive medical care of the highest quality, supported by a multidisciplinary team that includes radiation oncologists, neurosurgeons certified in radiosurgery, medical oncologists, medical physicists, and other highly trained professionals.

Additionally, all cases undergo a peer review process, ensuring clinical indications and treatment plans are evaluated by a tumor board before treatment begins. We utilize high-quality magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to ensure every detail is considered in the treatment plan, reinforcing our precision and care.
The certification confirms that Centro Médico ABC meets the highest international standards for safety, technology, and precision in radiosurgery procedures, with rigorous quality controls applied before, during, and after treatment. Because millimeters matter, we ensure our patients receive the best possible care.
What is Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)?
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) is an advanced and precise treatment used to treat intracranial lesions, performed by a multidisciplinary team that includes a radiation oncologist and a neurosurgeon accredited in radiosurgery. This technique allows for the application of high-precision radiation directly to the tumor in the brain, minimizing the impact on surrounding healthy tissue.
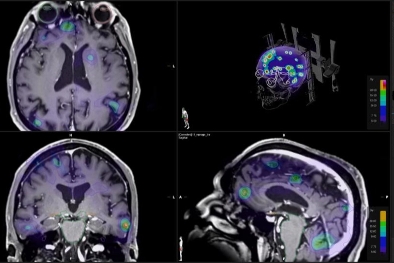
On the other hand, Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) is used to treat extracranial lesions, such as those in the lungs, liver, spine, and other areas. Like SRS, SBRT is performed with great accuracy, delivering high doses of radiation directly to the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. This treatment is carried out by a radiation oncologist and offers an effective, non-invasive option for treating tumors in various parts of the body.
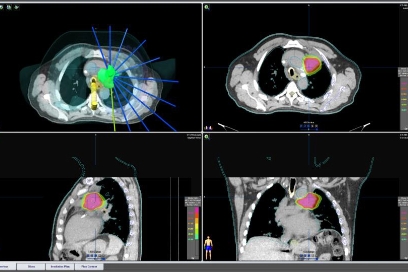
Both treatments, SRS and SBRT, are non-invasive options that allow for faster recovery, enabling patients to return to their daily activities more quickly, while providing an effective way to treat certain types of tumors. At our Cancer Center, we have state-of-the-art technology to carry out these procedures with the utmost precision and safety.
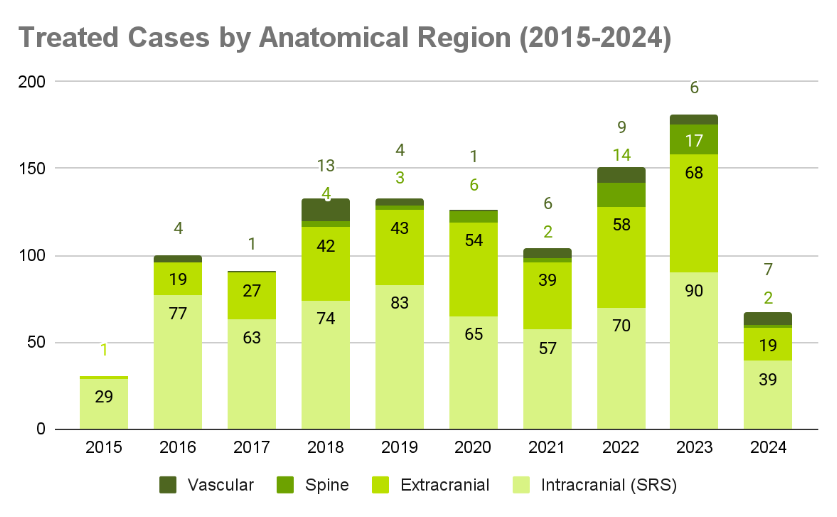
Cases Treated at ABC Medical Center (2015-2024)
At ABC Medical Center, we have been providing specialized care since 2015, treating thousands of cases with a comprehensive approach and positive results for our patients.
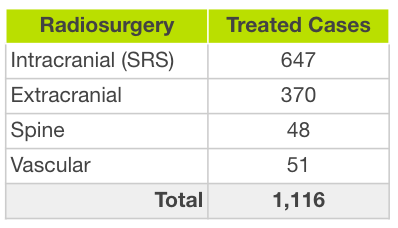
What pathologies can be treated with Radiosurgery (SRS)?
Brain Metastases (MTX SN): Brain metastases are tumors that originate in other organs, such as the lungs, breast, or prostate, and spread to the brain. Radiosurgery allows them to be treated with precision, helping to reduce their size or stop their growth without the need for invasive surgery.
Benign Pathologies of the Central Nervous System:
- Meningioma: A tumor that forms in the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
- Schwannoma: A tumor that grows on the nerves.
- Pituitary Adenoma: A tumor in the pituitary gland of the brain.
- Cavernoma: A lesion in the blood vessels of the brain.
- Paraganglioma: A rare tumor that develops in the adrenal glands and other organs.
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): AVMs are an abnormal collection of blood vessels that can cause brain hemorrhages. Radiosurgery is used to treat these malformations without the need for open surgery.
Functional Pathologies
- Trigeminal Neuralgia: Intense facial pain due to a problem with the trigeminal nerve.
- Epilepsy: A disorder in which people have recurrent seizures.
- Resistant Pain: Chronic pain that does not respond to other treatments.
Bone Metastases (MTX Bone – Spine): When tumors from other organs spread to the spine, radiosurgery can help treat these metastases precisely and effectively.
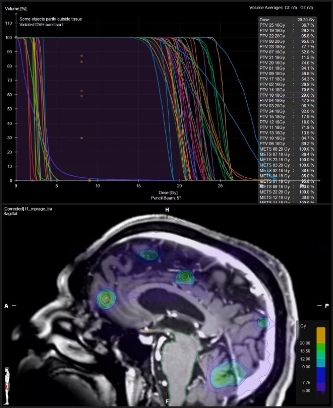
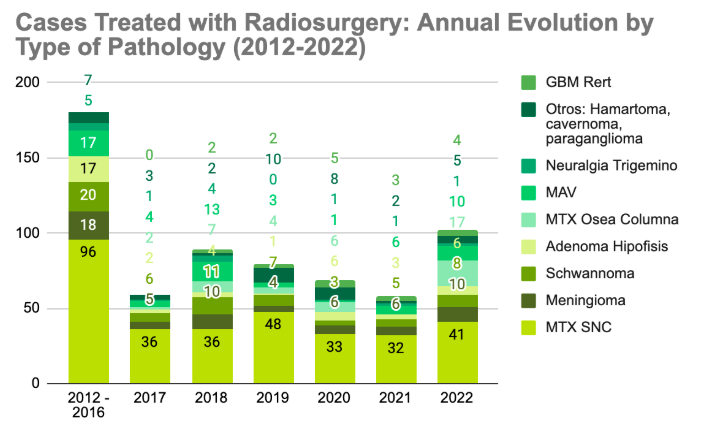
Cases Treated with Radiosurgery by Year (2012-2022)
The table shows the number of cases we have treated with radiosurgery at the Cancer Center, organized by type of pathology and year. This allows us to observe how the treatment of these conditions has evolved over time, and also how we have been able to assist patients with various brain and spinal conditions using state-of-the-art technologies.
Our Radiotherapy Unit stands out for being at the forefront and offering our patients the benefits of the latest advances in technology.
We have the first equipment in Latin America for Surface Guided Optical Positioning or SGRT (Surface Guided Radiation Therapy). SGRT uses an advanced visualization system of the external surface of the patient that allows real-time monitoring of the patient’s movements, ensuring that the radiation beam is only fired in the correct positioning.
We also have the only linear accelerator equipment that integrates an Image-Guided Radiotherapy (IGTR) verification system during radiosurgery treatments. The images it provides in 4D accurately determine the size and shape of the tumor, as well as its position in real time so that the radiation dose is delivered with sub-millimeter precision, significantly protecting healthy organs. It allows treating tumors that require exceptional precision, such as lung lesions, since it monitors the respiratory cycle, synchronizing the radiation to the movement of the tumor.
And we are embracing the new concept of Adaptive Radiation Therapy, in which the radiation dose is readjusted as tumor size shrinks during treatment, further reducing the risk of side effects, and one more step in High Precision Radiation Therapy
What is Radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation not for diagnostic purposes but at high doses with the therapeutic intent to kill cancer cells. Radiation can be external or internal. External radiation therapy is the most common form, we use equipment called linear accelerators and it is an outpatient treatment carried out in our Radiotherapy Unit. It is non-invasive, does not hurt, does not lose hair, and allows you to continue with daily activities after each session, without fear of emitting radioactivity.
We design your treatment through simulation and planning
Before the first session, you go to an appointment to design and individualize your treatment through simulation and planning. The objective of the simulation is to determine in a tomography equipment (CT simulator) that resembles the linear accelerator the position of your body that is repeatable and comfortable, with or without positioning accessories, which will be optimal for the sessions of your therapeutic course. In addition, computed tomography images that provide detailed information on the location of the tumor, tumor volume, structures surrounding the tumor, etc. are obtained. All this data is sent through the network to the treatment planner whose software or planning program reconstructs a computer model of your injury or injuries. On this virtual model, medical physicists and dosimetrists delimit the target volumes and the organs at risk (surrounding healthy tissues), calculate the precise doses and directions of the radiation beams that will be aimed at the tumor, and together with your radiation oncologist, define the specific treatment plan that will be sent to the linear accelerator without modification capacity and with detailed control.
Duration of the sessions
Sessions last approximately 30 minutes and shooting times are 1 to 2 minutes. Your radiation oncologist will let you know the number of sessions required to achieve the desired goal of your treatment.
At the end of your treatment
The patient’s care in radiotherapy does not end with the last session, when the full dose has been received, but continues with periodic consultations during which possible side effects are detected early and treated, which have a window from 4 to 6 weeks. Then, the response evaluation follow-up is carried out. Expected response times vary depending on the type of cancer, between 2 to 6 months.
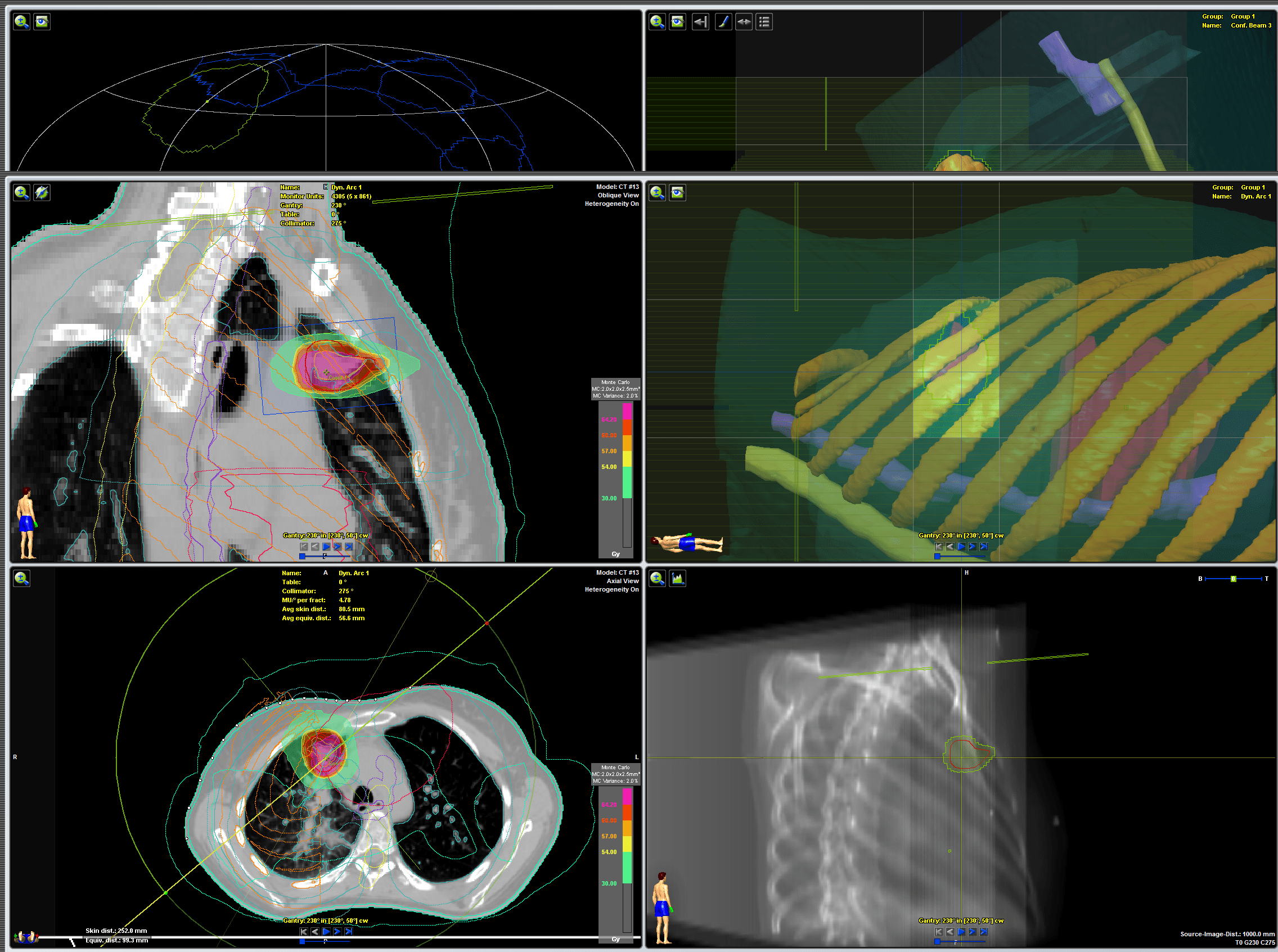
Virtual lung tumor planning. Medical physicists and dosimetrists have delineated the target volumes and organs at risk (surrounding healthy tissues) and calculated the precise dose distribution.
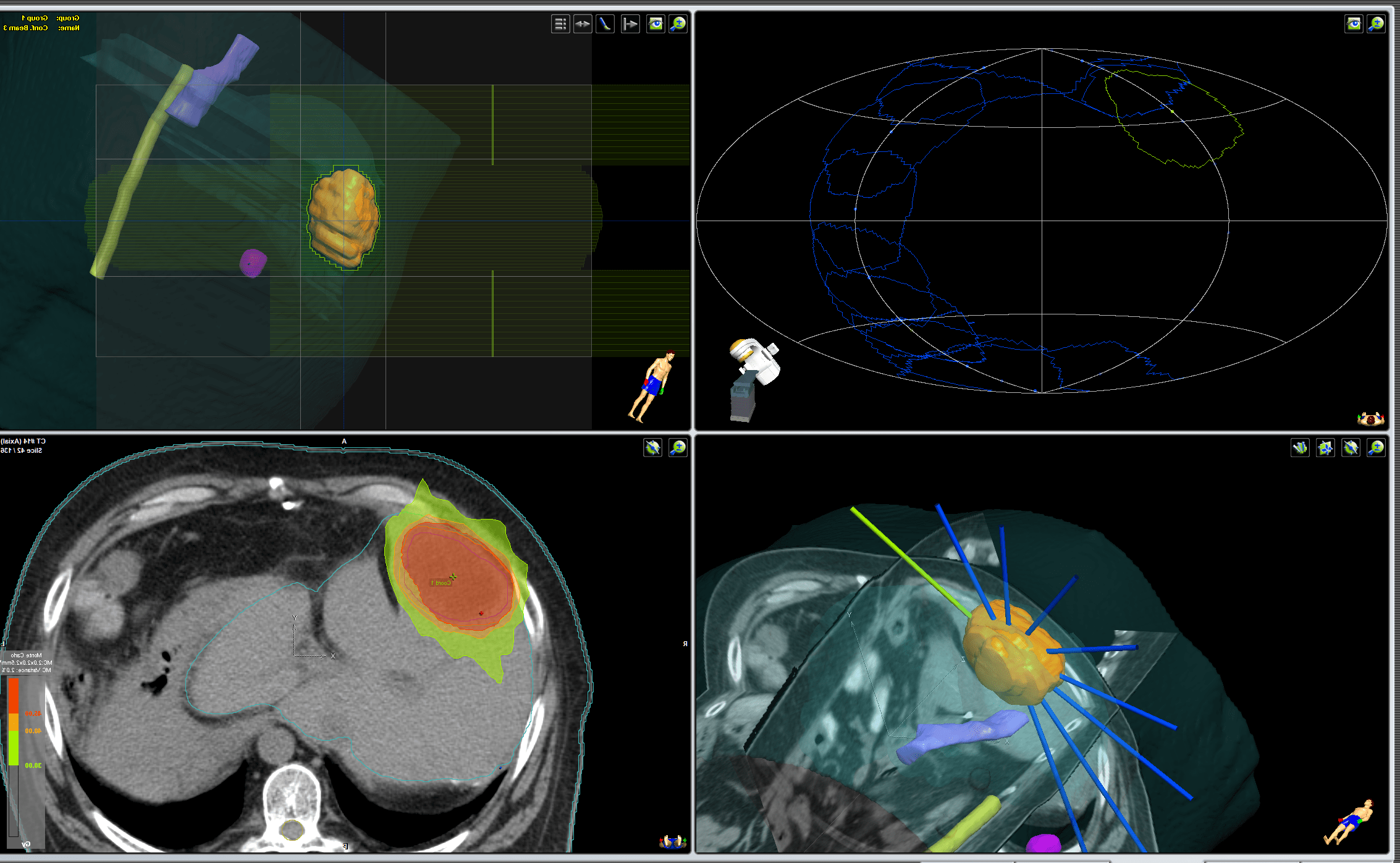
Virtual planning of liver tumor. Medical physicists and dosimetrists have delineated the target volumes and organs at risk (surrounding healthy tissues) and calculated the precise dose distribution as well as the directions of the radiation beams that will be aimed at the tumor.
¿En qué consiste la radioterapia?
Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation not for diagnostic purposes but at high doses with the therapeutic intent to kill cancer cells. Radiation can be external or internal. External radiation therapy is the most common form, we use equipment called linear accelerators and it is an outpatient treatment carried out in our Radiotherapy Unit. It is non-invasive, does not hurt, does not lose hair, and allows you to continue with daily activities after each session, without fear of emitting radioactivity.
Before the first session, you go to an appointment to design and individualize your treatment through simulation and planning. The objective of the simulation is to determine in a tomography equipment (CT simulator) that resembles the linear accelerator the position of your body that is repeatable and comfortable, with or without positioning accessories, which will be optimal for the sessions of your therapeutic course. In addition, computed tomography images that provide detailed information on the location of the tumor, tumor volume, structures surrounding the tumor, etc. are obtained. All this data is sent through the network to the treatment planner whose software or planning program reconstructs a computer model of your injury or injuries. On this virtual model, medical physicists and dosimetrists delimit the target volumes and the organs at risk (surrounding healthy tissues), calculate the precise doses and directions of the radiation beams that will be aimed at the tumor, and together with your radiation oncologist, define the specific treatment plan that will be sent to the linear accelerator without modification capacity and with detailed control.
Duration of the sessions
Sessions last approximately 30 minutes and shooting times are 1 to 2 minutes. Your radiation oncologist will let you know the number of sessions required to achieve the desired goal of your treatment.
At the end of your treatment
The patient’s care in radiotherapy does not end with the last session, when the full dose has been received, but continues with periodic consultations during which possible side effects are detected early and treated, which have a window from 4 to 6 weeks. Then, the response evaluation follow-up is carried out. Expected response times vary depending on the type of cancer, between 2 to 6 months.
Virtual lung tumor planning. Medical physicists and dosimetrists have delineated the target volumes and organs at risk (surrounding healthy tissues) and calculated the precise dose distribution.
Virtual planning of liver tumor. Medical physicists and dosimetrists have delineated the target volumes and organs at risk (surrounding healthy tissues) and calculated the precise dose distribution as well as the directions of the radiation beams that will be aimed at the tumor.
Types of Radiotherapy
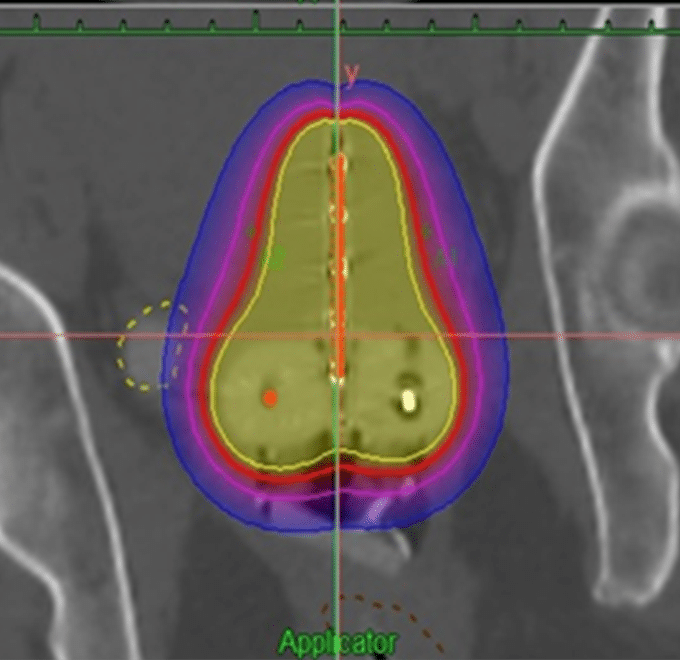
Brachytherapy
Unlike the other types of radiation therapy, brachytherapy is a form of internal radiation, generally used for small lesions. Radioactive material is placed in the area of the tumor or where a tumor was removed to sterilize the area. Depending on the dose, the location in the body, the type of cancer, among others, the radiation source can remain for a few minutes, several days, or indefinitely. Since the body emits radiation for some time, you will be instructed to follow safety measures. In our center we have outpatient Iridium 192 high-rate brachytherapy and 3D technique with less morbidity.
Brachytherapy
Unlike the other types of radiation therapy, brachytherapy is a form of internal radiation, generally used for small lesions. Radioactive material is placed in the area of the tumor or where a tumor was removed to sterilize the area. Depending on the dose, the location in the body, the type of cancer, among others, the radiation source can remain for a few minutes, several days, or indefinitely. Since the body emits radiation for some time, you will be instructed to follow safety measures. In our center we have outpatient Iridium 192 high-rate brachytherapy and 3D technique with less morbidity.

Radiosurgery
It is a virtual surgery, a non-invasive procedure that does not require anesthesia in which the tumor tissue is destroyed or eliminated by means of radiation. High doses are delivered faster, shortening radiation time, and with submillimeter precision, reducing exposure to healthy organs. It requires fewer sessions (1 to 8 sessions) of treatment than other types of radiation therapy.
Intracranial radiosurgery, known by its acronym SRS or Stereotactic Radiosurgery, and the corporal radiosurgery known by its acronym SBRT or stereotactic body radiotherapy.
We have experience in the treatment of oligometastasis (metastatic disease small in number and size), in which very selective and precise treatment with radiosurgery has shown benefit, in addition to being able to treat several lesions at the same time.
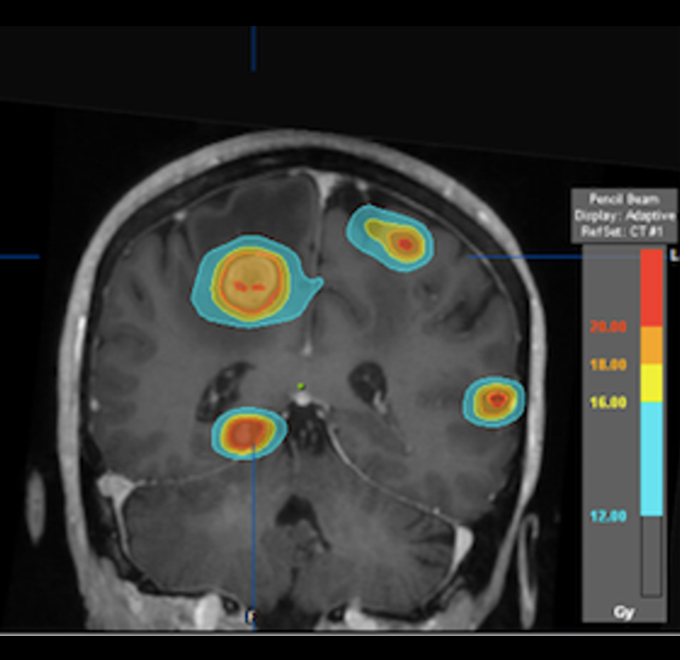
Radiosurgery
It is a virtual surgery, a non-invasive procedure that does not require anesthesia in which the tumor tissue is destroyed or eliminated by means of radiation. High doses are delivered faster, shortening radiation time, and with submillimeter precision, reducing exposure to healthy organs. It requires fewer sessions (1 to 8 sessions) of treatment than other types of radiation therapy.
Intracranial radiosurgery, known by its acronym SRS or Stereotactic Radiosurgery, and the corporal radiosurgery known by its acronym SBRT or stereotactic body radiotherapy.
We have experience in the treatment of oligometastasis (metastatic disease small in number and size), in which very selective and precise treatment with radiosurgery has shown benefit, in addition to being able to treat several lesions at the same time.

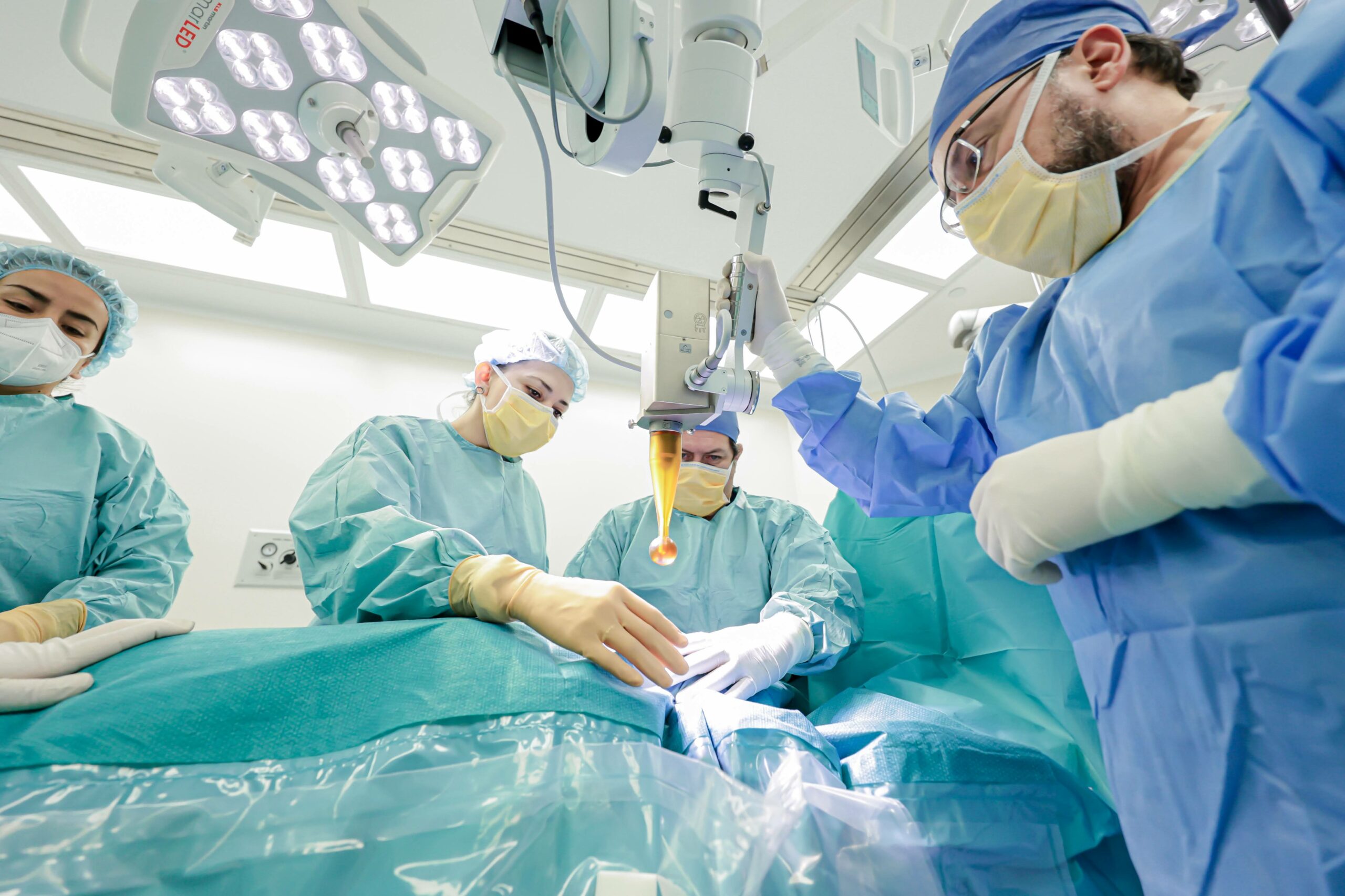
Intraoperative radiation therapy
We are the first private medical center to have INTRABEAM, a portable device used during surgery. In breast-conserving therapy, immediately after the tumor is removed, a sphere is placed in the surgical cavity. A single dose over approximately 30 minutes is equivalent to standard six-week external postoperative radiation therapy.
Intraoperative radiation therapy
We are the first private medical center to have INTRABEAM, a portable device used during surgery. In breast-conserving therapy, immediately after the tumor is removed, a sphere is placed in the surgical cavity. A single dose over approximately 30 minutes is equivalent to standard six-week external postoperative radiation therapy.
Pediatric Radiation Therapy
We are pioneers in high quality and precision Pediatric Radiation Therapy treatments to achieve success in the control of the disease and limit the possible side effects that may occur in the long term, with SBRT and brachytherapy.
Non-Oncological Radiation Therapy
We offer radiotherapy for non-oncological conditions in which it is indicated as a curative technique: arteriovenous malformations, pituitary adenoma, schwannoma, keloids.
Intensity Modulated Radiation (IMRT)
High-precision radiation therapy that seeks to control or modulate the intensity and direction of small radiation beams so that they adapt with great precision to the shape of the tumor, delivering the highest dose of radiation to the tumor target, minimizing the exposure of surrounding healthy organs and tissues.
Total body irradiation
TBI (Total Body Irradiation) consists of irradiating the entire body of the patient in a homogeneous way, being part of the conditioning process for bone marrow transplantation and the treatment of some hematological diseases such as leukemia, lymphoma, or multiple myeloma.
We are the first center in Mexico to use VMAT for this procedure with more than 30 cases in which less acute toxicity was observed during the procedure.
VMAT/Rapid Arc
It is an advanced IMRT technique, in which the device rotates around the patient a specified number of times. In this way, it is possible to treat the tumor from different angles, with high dose precision, shortening the treatment time.
Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy
During 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, the beams deliver a fixed dose and adapt to the shape of the tumor.
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy
Larger doses are administered in fewer sessions than in standard radiotherapy (5 vs 25 sessions).
Where to Find Us

Campus Observatorio
Sur 136 No. 116, Col. Las Américas, Álvaro Obregón, 01120, Cd. de México.