What is aortoiliac obstructive artery disease?
This disease occurs when the aortic artery, our body’s main vessel, is blocked. The iliac arteries are the most distant branches of the aorta which divides at the navel and carries blood to the limbs and the pelvic organs. This blockage is usually caused by the formation of fatty, cholesterol, and calcium plaques within the walls of these blood vessels.
Symptoms of aortoiliac obstructive artery disease
Peripheral artery disease occurs in about 15% to 20% of people over the age of 65.
For symptoms to exist, these arteries’ lumen has to be blocked above 60% or 70%, therefore there may be no symptoms at first, if it progresses, later there may be fatigue, pain, or cramps when walking or going up or down the stairs. Other symptoms can be erectile dysfunction.
When it is severe, it can cause pain in the feet and toes at rest, as well as cold, numbness, and the formation of ulcers that can progress to gangrene, including tissue death.
Causes of aortoiliac obstructive artery disease
The most common cause of aortoiliac disease is atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
When these symptoms appear, it is important to see a vascular surgeon who will take a complete medical history and physical examination.
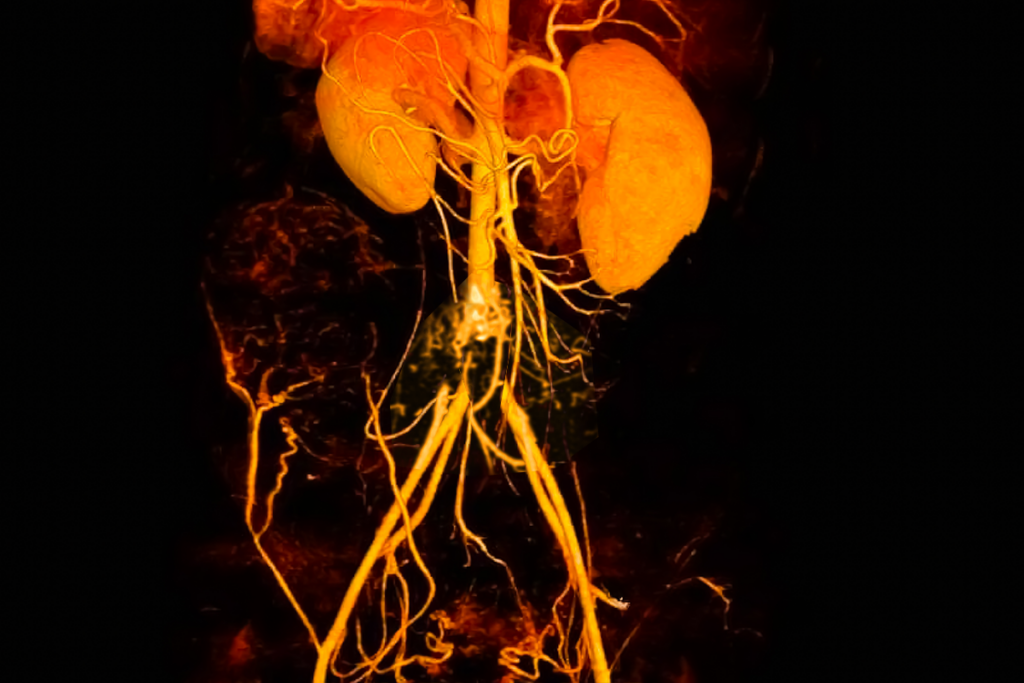
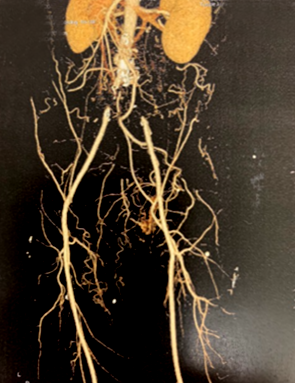
An ultrasound of the abdominal aorta and arterial vessels of the limbs and a CT angiography should be performed. With these tests, the obstruction can be located and decide on the treatment.
Treatment of aortoiliac obstructive artery disease
Aortoiliac obstructive disease tomography
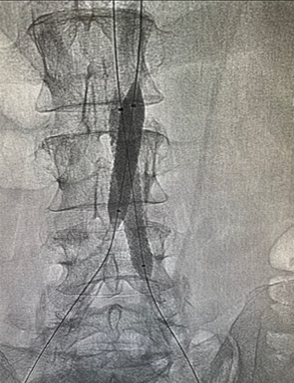
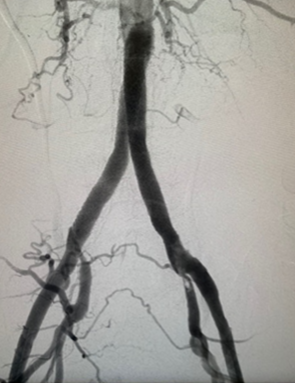
Aortography with stenting
Final score
When the aortoiliac obstructive disease is mild to moderate, treatment can be conservative, modifying risk factors such as quitting smoking, controlling cholesterol, controlling blood pressure, and a progressive exercise program.
Some medications are generally prescribed such as aspirin, which is a platelet inhibitor, and statins that help us reduce cholesterol and the progression of plaque in these vessels.
In moderate or severe situations, minimally invasive procedures, such as angioplasty, can be performed, which is the dilation of these areas with an intravascular balloon and the placement of stents. Stents are a type of spring that generally compresses the plaque against the wall, creating a larger lumen of the blood vessel.
On some occasions, the creation of a surgical bridge is required to skip the blocked area.
At ABC Medical Center’s Cardiovascular Center, we can provide you with specialized care. Contact us!
Fuente: Dr. Salomón Cohen Mussali – Médico especialista en Cirugía Vascular y Endovascular del Centro Médico ABC.