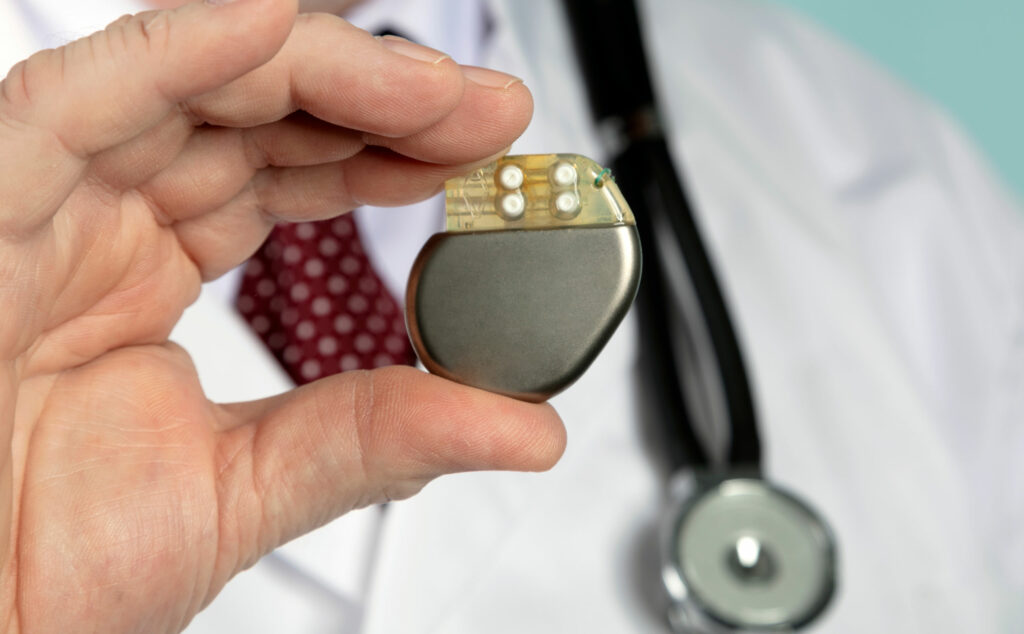
People often ask themselves, what is the use of a pacemaker? The pacemaker, also known as a cardiac pacing device, helps control the heartbeat, as long as it is placed on the chest. By using it, the organ is prevented from beating too slowly.
The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. Both right and left ventricles, along with the electrical system, are responsible for keeping the heart beating at an adequate rate, between 60 and 100 beats per minute in an adult. If the heart cannot do this on its own, the doctor may order the use of a pacemaker.
In the event that the heart suffers some type of damage to its electrical system due to aging, a heart attack, some medications, or even genetic conditions, the heart rhythm may become irregular.
So, placing a pacemaker will make it possible to control the heartbeat in patients suffering from a pathological cardiac arrhythmia, mainly in cases of bradycardia, when it beats too slowly; although it can also be indicated in patients who have irregular heartbeats or tachycardia.
How does a pacemaker work?
Pathological bradycardia is the main cause when determining the use of a pacemaker, which will allow the heart rate to be restored by increasing it when necessary, preventing future complications.
The traditional pacemaker consists of three parts, each with a specialized function:
- Cables. They are implanted inside the veins and allow impulses to be carried to the heart.
- Electrodes. They detect the natural heartbeat and send electrical impulses based on the intensity of the heartbeat.
- Pulse generator. Metallic container that houses a battery and the electrical circuit to control the electrical impulses and their frequency, which will be sent to the heart.
Types of pacemakers
There are different varieties of devices that will help regulate the heart rate depending on each patient’s needs and the necessary duration.
- Biventricular pacemaker. Both the right and left ventricle will receive electrodes. This device is part of cardiac resynchronization therapy in patients who are developing heart failure problems due to severe bradycardia.
- Single chamber pacemaker. Its electrodes are placed in a single chamber of the heart, which is usually the right ventricle.
- Dual chamber pacemaker. The electrodes are placed in two chambers of the heart, normally the right ventricle and atrium.
- Endocavitary pacemaker. Also known as an intravenous pacemaker, its electrodes are inserted through a central vein until they reach the endocardium, the generator is implanted subcutaneously.
- Wireless pacemakers. It does not have wires; it is implanted directly into the heart muscle to generate the pulses that will travel through the veins.
- Permanent pacemaker. This pacemaker will be permanent due to the existence of a chronic heart disorder without the possibility of the heart being able to restore its normal frequency.
- Temporary pacemaker. It is implanted temporarily in patients who suffer from potentially serious but not chronic irregularities, offering help in a specific period of time, such as surgery or after a heart attack.
- Transcutaneous pacemaker. Temporary pacemaker where the electrodes are placed on the skin, no surgical implantation is needed.
At ABC Medical Center’s Cardiovascular Center, we can provide you with specialized care and solve all your doubts such as what a pacemaker is for. Contact us!
Fuente:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/es/tests-procedures/pacemaker/about/pac-20384689
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/es/salud/marcapasos/como-funciona