Arrhythmia Clinic
Location:
Consulting Room 15, 2nd floor of the Central Tower at Campus Observatorio.
Hours of operation:
Monday to Friday from 08:00 to 17:00 hrs
At the ABC Arrhythmia Clinic, our electrophysiology specialists handle the diagnosis and treatment of heart rhythm disorders. Arrhythmias are divided into two main categories: tachyarrhythmias (fast rhythms) and bradyarrhythmias (slow rhythms).
Some of the most common types of arrhythmias include:
Tachyarrhythmias (fast rhythm):
- Atrial Fibrillation: Rapid and irregular beats in the atria.
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT): Sudden episodes of fast rhythm above the ventricles.
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Fast rhythm originating in the ventricles, potentially dangerous.
- Ventricular Fibrillation: Disorganized and very fast rhythm that prevents the effective pumping of blood.


Bradyarrhythmias (slow rhythm):
- Sinus Bradycardia: Slow heart rhythm originating in the sinus node.
- Atrioventricular (AV) Block: Problems in the conduction of heart impulses with three degrees of severity.
- Sinoatrial Node Dysfunction: Irregular or slow rhythm due to issues in the sinus node.
Other Types:
- Extrasystoles: Additional beats that interrupt the normal rhythm.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome: Abnormal electrical connection that causes a fast rhythm.
Why choose ABC Arrhythmia Clinic?
Evaluation and Diagnosis
The ABC Medical Center has a specialized cardiovascular diagnostic center focused on the evaluation, diagnosis, and monitoring of diseases and disorders of the cardiovascular system.

Featured Treatments
Cardioversion: Cardioversion is a medical procedure that restores a normal heart rhythm in people with certain types of heart rhythm abnormalities (arrhythmias). It is often performed by delivering electrical shocks to the heart through electrodes placed on the chest.
Catheter Ablation: Cardiac ablation is a procedure aimed at eliminating (through precise destruction and scarring) small areas of the heart that cause or sustain an irregular rhythm.
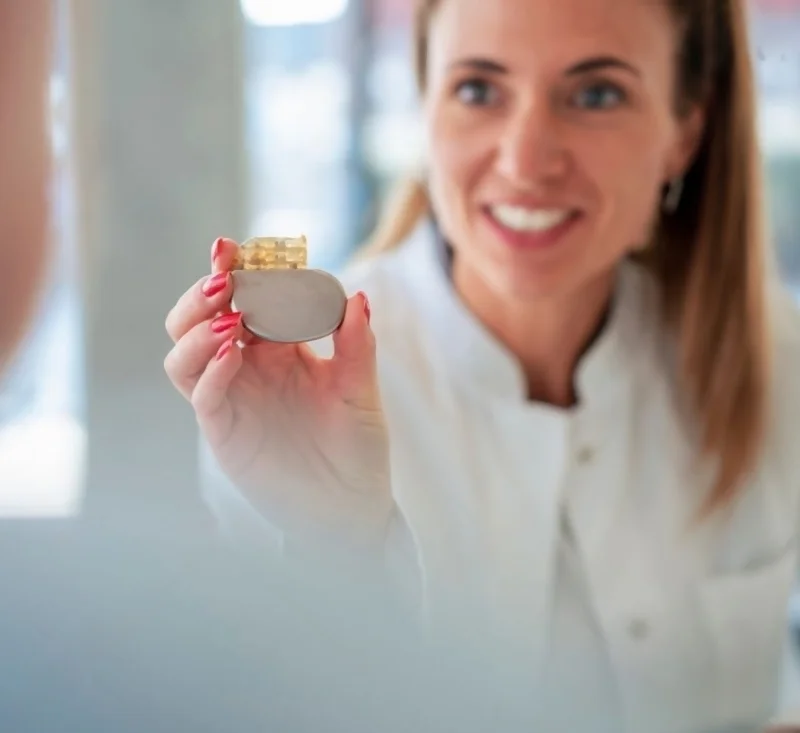
Pacemaker: Pacemakers are devices that regulate the heart rate or treat dangerous arrhythmias.

Equipment and Technology
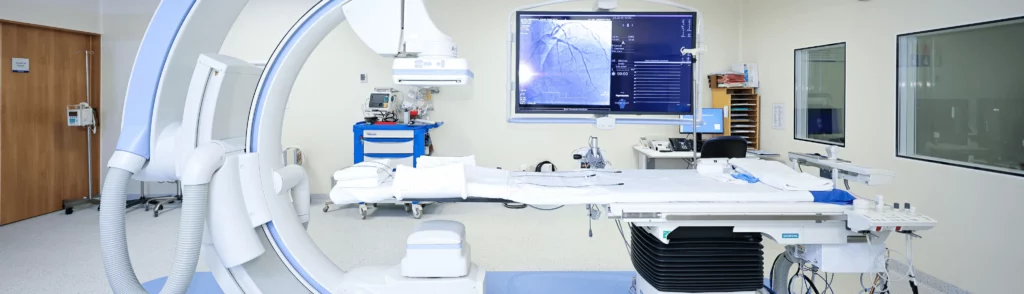
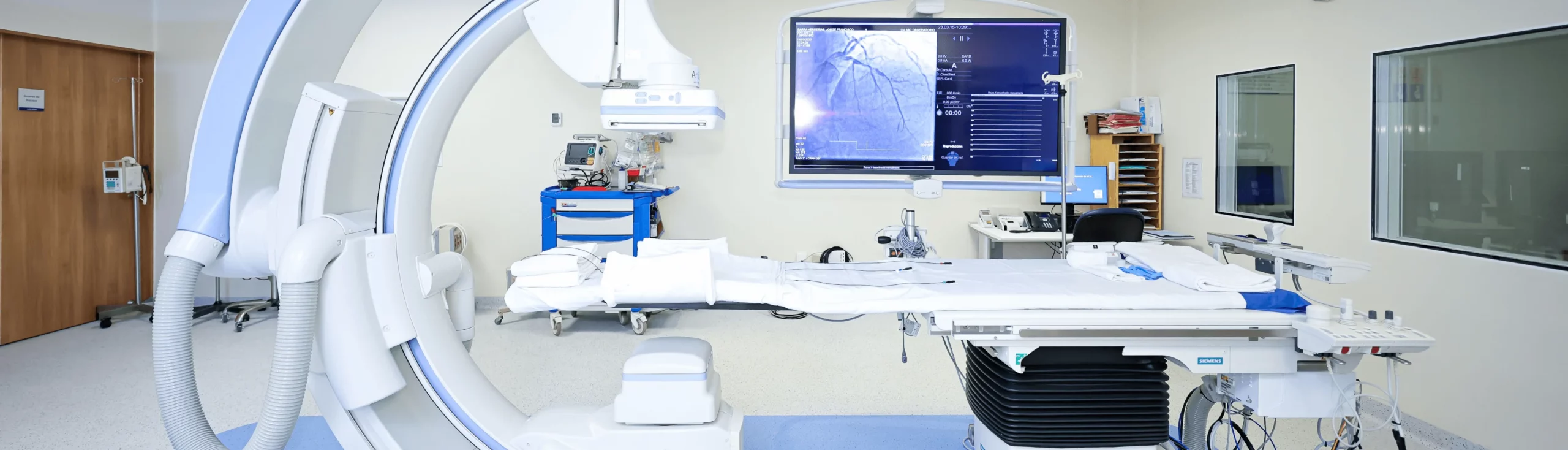
State-of-the-art equipment: We use advanced technology such as electroanatomical mapping, which allows us to obtain real-time three-dimensional images of the patient’s heart, along with crucial electrophysiological information to perform more precise and successful procedures.
Cardiovascular Interventional Rooms (CATH-LAB): We have spaces dedicated to catheter ablation and the insertion of implantable devices, designed to carry out interventions with the highest effectiveness and safety.
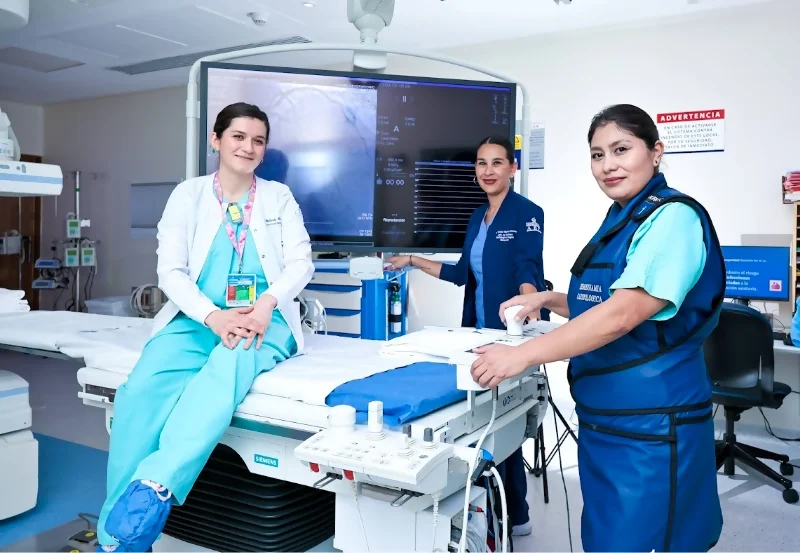

Specialized Staff
Electrophysiologist Cardiologists and Support Staff: Doctors and technicians specialized in the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias. Find a specialist in our directory:
Syncope Clinic
Syncope is a sudden and brief loss of consciousness with the absence of postural tone, followed by spontaneous recovery. The patient remains immobile and limp, generally has cold limbs, a weak pulse, and shallow breathing. Occasionally, brief involuntary muscle jerks occur, resembling a seizure.
The ABC Syncope Clinic offers comprehensive care to identify and treat the causes of syncope, improve patients’ quality of life, and reduce the risk of future episodes.
Structural Intervention Clinic (Valvular)
We have doctors specialized in heart diseases (cardiologists), cardiac surgery (cardiac surgeons), and other specialists who collaborate to evaluate your condition. Interventional specialists and imaging diagnosticians in cardiology work together to provide care according to your needs.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI)
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has become the treatment of choice for patients with severe aortic stenosis who are considered inoperable or at high surgical risk, with better outcomes than conservative management, including aortic valvuloplasty.
What is a valve disease?
Every time the heart beats, blood enters the heart, circulates through it, and then leaves. Moreover, the heart pumps about 100 gallons (379 liters) of blood into the body every hour. Two types of problems can alter the flow of blood through the valves: regurgitation and stenosis.
Regurgitation
Is also called “insufficiency” or “incompetence”. Regurgitation occurs when a valve does not close properly and allows blood to leak backward, rather than flow, in a unidirectional manner, as it should. If too much blood flows backward, only a small amount of blood can flow to the organs of the body. The heart tries to compensate by working harder, but over time the heart enlarges (dilates) and its ability to pump blood to the body decreases.
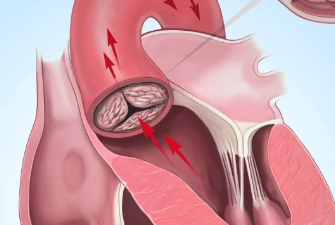

Stenosis
Is when the leaflets do not open wide enough and only a small amount of blood can pass through the valve. Stenosis occurs when the leaflets thicken, harden, or fuse together. Due to the narrowing of the valve, the heart must work harder to pump blood to the body.
Some of the most common conditions that occur in the valve clinic are:
- Congenital heart disease
- Structural heart diseases
- Acute coronary syndromes
At the Cardiovascular Center we offer you a wide range of prevention, diagnosis, timely treatment and follow-up services to take care of your heart and that of your loved ones
Heart Failure Clinic
Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle does not pump blood as well as it should. Certain conditions, such as narrowed arteries in the heart (coronary artery disease) or high blood pressure, progressively leave the heart too weak or stiff to fill and pump effectively. Not all conditions that cause heart failure can be reversed, but treatments can improve the signs and symptoms of heart failure and help you live longer.
Lifestyle changes (such as exercising, reducing sodium in your diet, managing stress, and losing weight) can improve your quality of life. One way to avoid heart failure is to prevent and control the conditions that cause it, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, or obesity.
Cardiac Rehabilitation We offer individualized treatment according to your functional capacity.
Cardiac rehabilitation includes a series of physical activities, relaxation and education for the modification of risk factors, aimed at secondary prevention, as a way of limiting damage and improving quality of life.
At the ABC Medical Center we develop a cardiac rehabilitation program that can improve the functioning capacity of your heart, returning to a productive and satisfactory life by decreasing the level of stress, increasing your confidence and desire to live, as well as reducing the incidence of cardiovascular events.
What achievements will you obtain with a cardiac rehabilitation program?
- Improve your physical capacity.
- Create exercise habits.
- Modification of risk factors.
- Improves lipid level.
- Control your body weight.
- Control blood glucose.
- Control blood pressure.
- Control or eliminate tobacco consumption.
- Reduce stress, anxiety and depression.
- Post acute myocardial infarction.
- Post-bypass surgery.
- Stable angina pectoris.
- Heart or lung transplant.
- Post-operative angioplasty or valve surgeries.
- Cardiomyopathies.
- Cardiac arrhythmias.
- Pacemaker.
- Heart failure.
- Postoperative angioplasty with or without stent.
- Postoperative cardiac catheterization.
Where to Find Us

Campus Observatorio
Sur 136 No. 116, Col. Las Américas, Álvaro Obregón, 01120, Cd. de México.

Campus Santa Fe
Av. Carlos Graef Fernández 154, Col. Santa Fe, Cuajimalpa, 05300, Cd. de México.