Learning how to measure glucose is essential for people with diabetes, a chronic disease that affects the body and its way of turning food into energy. To achieve this, it would have to break down food into glucose (sugar) and then release it into the bloodstream.
The pancreas is the organ responsible for insulin production, which is a hormone that allows glucose to move into the cells. The pancreas of people with diabetes may not produce enough insulin or their bodies cannot use it effectively.
To learn how glucose is measured, you have to know that there are different equipment and procedures.
Equipment:
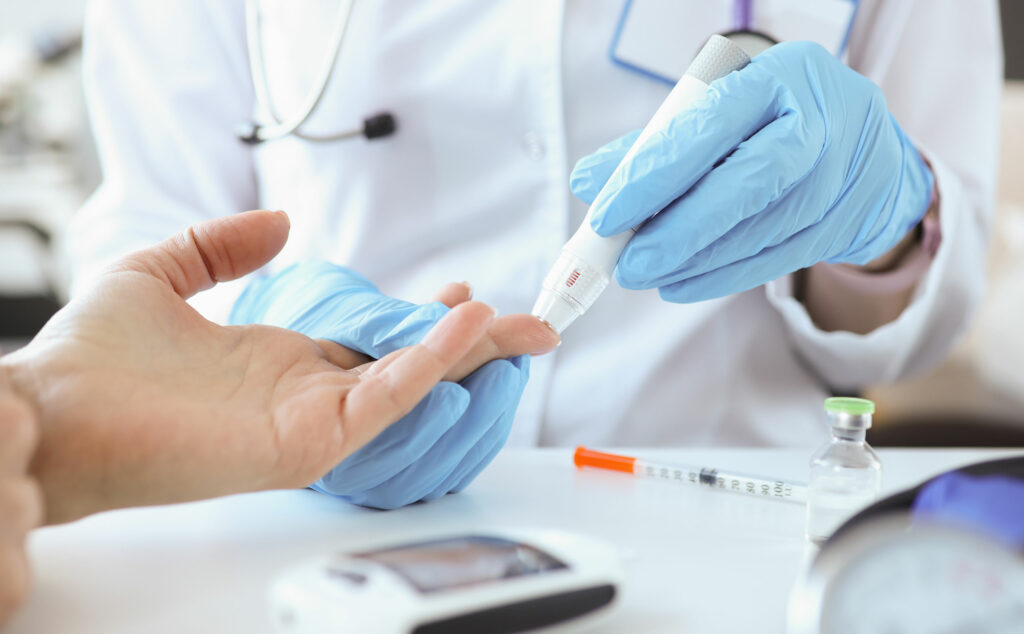
- Glucometer. The best-known and used meters; it requires a small blood sample taken from the finger.
- Continuous glucose meter (CGM). A device that allows measuring glucose in the interstitial fluid / between cells), is a relatively new technology and helps to understand how glucose moves.
- Flash-type glucose meter. It also takes measurements through the interstitial fluid and lasts longer than the CGM.
Lab tests:
- A1c Tests. Also known as a hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, it is a blood laboratory test that measures the average blood sugar of the last three months.
- Blood sugar test. Measures blood sugar levels and allows you to find out if they are within healthy limits. It is also known as a fasting glucose test.
What are normal glucose levels?
The World Health Organization (WHO) indicates that a normal range of fasting blood sugar is between 70 and 100 mg/dl (milligrams per deciliter); a range between 101 and 125 mg/dl is impaired fasting glucose, something that could be considered as pre-diabetes; and a range of 126 mg/dl or higher is diabetes.
Although this is the “normal” range, it should be considered that what constitutes normal blood sugar levels varies in each person depending on their age, physical activity, medications, or even the existence of some type of medical condition.
For a quick blood sugar measurement it is necessary to use a glucometer. In general terms, the following steps must be followed for its use:
- Wash and dry your hands (food and dirt can alter the results).
- Insert a test strip into the glucometer.
- Using a lancet, prick the chosen finger.
- Directly place a drop of blood on the lancet.
- Check the glucometer for blood sugar levels.
Why does glucose rise?
Many factors can cause hyperglycemia, high blood sugar, in people with diabetes; these might be:
- Physical activity.
- Some diseases, infections, injuries, or surgeries.
- Some medicines, mainly those that contain steroids.
- Hormone changes.
- Dehydration.
- Food choice.
- Stress.
- Skipping a dose or insufficient doses of medication.
- Incorrect use of medications.
If you have high or low blood sugar numbers, it is best to go to your trusted doctor for assessment and the creation of a plan to follow.
At ABC Medical Center’s Diabetes Clinic, we can provide you with specialized care in case you have questions about how glucose is measured. Contact us!
Fuente:
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/spanish/living/bloodglucosemonitoring.html
https://www.mayoclinic.org/es/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/blood-sugar/