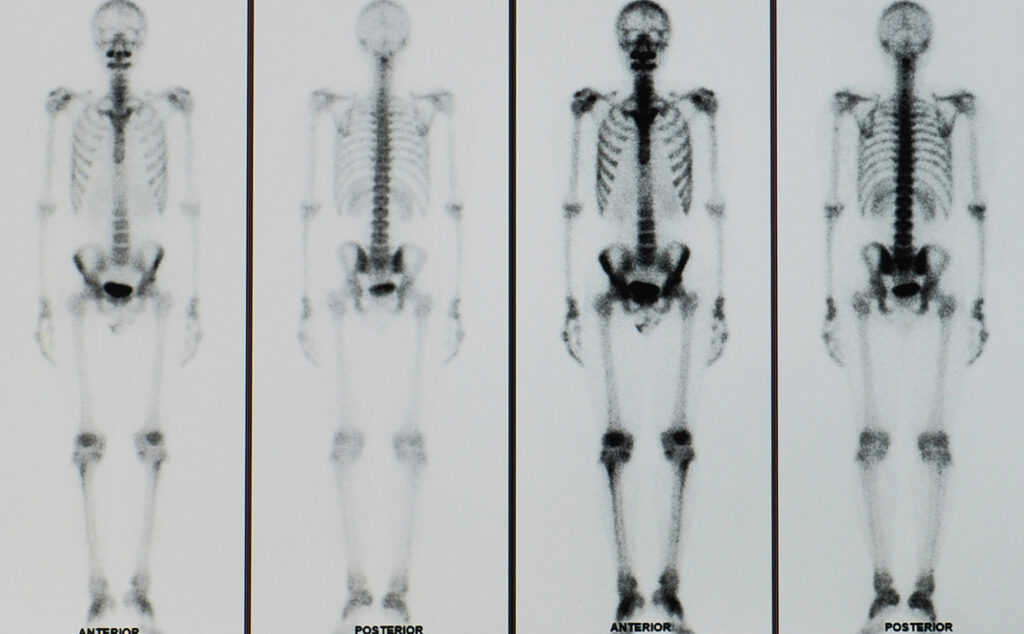
A bone scan is especially useful when bone cancer and other skeletal disorders are suspected.
Bone scan
A bone scan is a test that aids in the diagnosis and evaluation of a variety of bone diseases or conditions.
Nuclear medicine images are used, which implies the use of small amounts of radiotracers (radioactive substances), a camera that detects radioactive activity, and a computer that allows the bones to be seen.
The bone scan is useful for detecting cancer that has started in or spread to the bone. It seeks to help diagnose the cause of bone pain for which no explanation has been found.
What is a bone scan?
It is a nuclear medicine imaging study that helps diagnose various types of bone diseases, for example, to detect causes for bone pain that have no explanation.
Thanks to the complete exploration of the skeleton, it can be possible to diagnose a wide range of disorders such as:
- Arthritis
- Cancer originating in or spreading to the bones
- Paget’s disease of bone
- Fractures
- Infections in the joints, prostheses, or bones
- Unexplained bone pain
If bone cancer is suspected, a bone scan provides especially useful results, since both primary cancer and bone metastases can be found.
This tool can also find bone changes sooner than can be seen with a conventional X-ray.
How is a bone scan performed?
The test is performed with the support of a specially trained and certified nuclear medicine technician. Its procedure involves an injection of small amounts of radioactive material.
Once the due time has elapsed, a mechanical arm that holds a camera sensitive to the radiotracers will move and explore the body.
After the tests, the radiologist (specialist in the interpretation of images) will look for signs of additional bone metabolism or bone cancer.
If something abnormal is detected, darker areas of “hot spots” and lighter areas of “cold spots” will appear on the images, showing the accumulation of radioactive markers or not.
A bone scan is highly sensitive to differences in bone metabolism but is less helpful in determining the exact cause of abnormalities, requiring additional testing to determine the cause of “hot spots”.
Generally speaking, a bone scan is painless and rarely has significant discomfort or side effects.
Through the natural process of radioactive decay, the small amount that was injected into the body will come out in the urine or feces within a couple of days after the procedure.
Fuentes:
https://centromedicoabc.com/centro-de-cancer/deteccion-de-cancer/
https://www.radiologyinfo.org/es/info/bone-scan
https://www.mayoclinic.org/es/tests-procedures/bone-scan/about/pac-20393136
https://www.cancer.net/es/desplazarse-por-atenci%C3%B3n-del-c%C3%A1ncer/diagn%C3%B3stico-de-c%C3%A1ncer/pruebas-y-procedimientos/gammagraf%C3%ADa-%C3%B3sea