Contact us
Precision Medicine
-
Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare Professionals
Credentialing Requirements
- About ABC
-
Inclusive Health
- ABC Talent
- ABC Foundation I.A.P
- Contact
- ES
What are Myomas and Cysts?
9 October 2025
Myomas and ovarian cysts are two common conditions, and most women experience one of them at some point in their lives. However, they are often confused with each other, but they are actually very different.
Also known as fibroids or leiomyomas, myomas are nodular growths that arise from a buildup of cells in the myometrium, the wall of the uterus.
They are considered benign tumors with a high incidence (about 50%) in women over 40 with risk factors such as overweight and obesity, alcohol consumption, and a family history of myomas.
Myomas are classified according to their location:
- Intramural myomas: Located within the wall of the uterus.
- Submucosal myomas: Protrude into the inner part of the uterus.
- Subserosal myomas: Develop on the outside of the uterus. These are the ones that cause heavy bleeding.
Symptoms and treatment vary depending on the type of myoma, but they are not usually serious or cause intense symptoms.
An ovarian cyst, on the other hand, is a fluid-filled, sac-like structure. It generally does not cause symptoms and does not require any treatment.
There are different types of cysts, with the most common being:
- Follicular cysts: Follicles are small sacs that store eggs. When they develop but do not release an egg, they turn into cysts that are not risky and do not require treatment.
- Corpus luteum cysts: When the follicle breaks open and releases the egg, the broken follicular structure is called the corpus luteum, which can cause bleeding.
- Dermoid cysts: These are benign tumors that are not related to menstruation, unlike the previous two types.
Signs and symptoms Myomas and Cysts
Uterine myomas often do not cause symptoms, but when they do, they can include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, or pelvic pressure. It’s also possible to experience frequent urination due to pressure on the bladder and, in more severe cases, pain during sexual intercourse or difficulty becoming pregnant. The type and intensity of symptoms vary depending on the size, location, and number of myomas.
Ovarian cysts, on the other hand, usually disappear on their own and do not cause symptoms. However, if they grow or rupture, they can cause sharp or intermittent pelvic pain, as well as a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, changes in the menstrual cycle, and pain during or after sexual intercourse. If ovarian torsion develops, it can cause sudden, intense pain that requires immediate medical attention.
Although both conditions can cause similar discomfort, their nature and origin are different. Myomas form in the uterus and are related to muscle tissue, while cysts appear in the ovaries and are more likely to be functional structures or a result of the ovulation process.
Diagnosis Myomas and Cysts
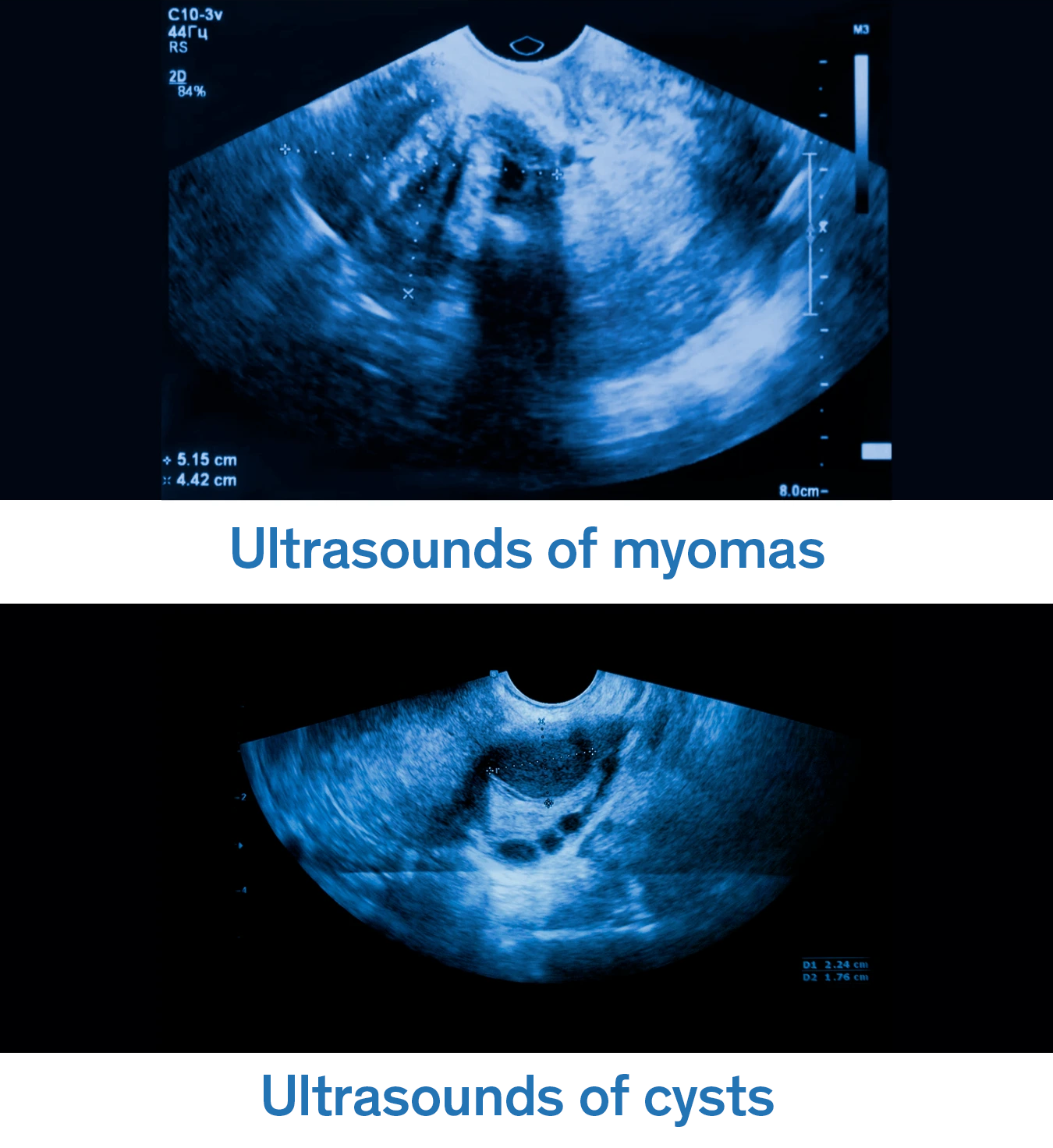
Uterine myomas are usually diagnosed during a routine gynecological exam when the doctor detects an increase in the size of the uterus. To confirm the diagnosis, imaging studies like a transvaginal ultrasound are often ordered to visualize the size, number, and location of the tumors. An MRI may also be used to get a more detailed image, especially if surgical treatment is being considered or if the myomas are very large.
For ovarian cysts, the diagnosis is made using imaging studies, with a pelvic or transvaginal ultrasound being the most common and effective method. This allows the doctor to observe the shape, size, fluid or solid content, and characteristics of the cyst. All of this helps determine if it is a functional cyst that will disappear on its own, or if it requires monitoring or intervention. If malignancy is suspected, hormonal tests or tumor markers like CA-125 may be requested, along with complementary imaging studies.
Treatment Myomas and Cysts
Treatment for uterine myomas depends on the size, location, number of tumors, severity of symptoms, and whether the patient wishes to preserve their fertility. In cases of mild or no symptoms, intervention is not always required, and only periodic medical monitoring is performed. But if the symptoms are bothersome, hormonal medications can be used to reduce bleeding or the size of the myomas. When medical treatments are not effective or in cases where the myomas are very large, options include procedures such as a myomectomy, which is the removal of the myomas while preserving the uterus, uterine artery embolization, or, in extreme cases, a hysterectomy, which is the removal of the uterus.
As for ovarian cysts, most are functional and disappear over time. But if the cyst persists, causes pain, or has suspicious characteristics, the doctor may recommend ultrasound monitoring or the use of hormonal medications to prevent new cysts from forming. When a cyst is painful, large, or does not disappear on its own, or if there is a suspicion of malignancy, a surgery such as an ovarian cystectomy to remove the cyst while preserving the ovary, or the removal of the affected ovary, may be performed.
At the Women’s Center at ABC Medical Center, we can provide you with specialized care. Contact us!
Fuentes:
How can we help you?

Ricardo Ostos
Content CreatorRicardo can convey complex medical information in an accessible and friendly way so that all of our patients can understand and benefit from it. In addition, he has an empathetic approach, offering information and practical advice that really makes a difference in people's lives. #lifebringsustogether.
Learn more about Ricardo on LinkedIn
Pay in interest-free monthly installments in Specialty Centers, Check Ups, Diagnostic Tests, and Hospitalization
Get from 3 to 9 interest-free installments* with American Express or 6 installments* when paying with Banamex, BBVA, HSBC, Santander or 12 installments*
when paying with Banamex.
Privacy Overview
Error: Contact form not found.
We help you
Send us your request and we will forward it to our specialists. We will get in touch with you very soon.
If you have preferred times to receive our call, please indicate them in your message.
Thank you for contacting us!
Interest-free
months in:
Interest-free
months in:
Specialty Centers
Diagnostic Studies
Check-ups
Hospitalization1
Choose from3 to 9 months when paying with American Express cards 2. Or
6 months when paying with your credit card3 Banamex, BBVA Bancomer, HSBC, Santander.
Or 12 months exclusively when paying with Banamex3
Valid until December 31, 2025. Promotions not cumulative. Subject to restrictions 1. In hospitalization, medical fees are not included. 2. Minimum amount: $1,500 for 3 to 6 months and $3,000 for 7 to 9 months 3. Minimum amount $1,500. (Cards issued abroad are not eligible).
Comparison of COVID-19 vaccines
Pfizer-
BioNTech
Pfizer-BioNTech
What is its effectiveness and what does it refer to?
Vaccine type: mRNA
Effectiveness: 95% after the second dose in the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19.
No Does not contain egg, latex, or preservatives.
How many doses are needed?
Two doses are needed, at least 21 days apart (or up to six weeks apart, if necessary).
Who should or shouldn’t get the vaccine?
People who should receive the vaccine are those over 16 years old.
People who should not receive the vaccine are those who have a history of anaphylactic shock (severe allergy) or who are allergic to any component of this vaccine such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) or polysorbate.
What are the possible side effects of the vaccine?
Pain where the injection was given, fatigue, headache, muscle pain, chills, joint pain, fever, nausea, malaise, and swollen lymph nodes.
How long will it take for me to be protected and what does it protect me from?
After 14 days of having the complete scheme (after the administration of the 2nd dose), the protection period is still under study. It protects us from serious COVID-19 or requiring hospitalization.
Moderna
What is its effectiveness and what does it refer to?
Vaccine type: mRNA
Effectiveness: 94.5% after the second dose in the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19.
Does not contain egg, latex, or preservatives.
How many doses are needed?
Two doses are needed, at least 28 days apart (or up to six weeks apart, if necessary).
Who should or shouldn’t get the vaccine?
People who should receive the vaccine are those over 18 years old.
People who should not receive the vaccine are those who have a history of anaphylactic shock (severe allergy) or who are allergic to any component of this vaccine.
What are the possible side effects of the vaccine?
Pain where the injection was given, fatigue, headache, muscle pain, chills, joint pain, fever, nausea, and swollen lymph nodes in the arm in which you received the injection.
How long will it take for me to be protected and what does it protect me from?
After 14 days of having the complete scheme (after the administration of the 2nd dose), the protection period is still under study. It protects us from serious COVID-19 or requiring hospitalization.
Janssen/
Johnson
& Johnson
Janssen/ Johnson & Johnson
What is its effectiveness and what does it refer to?
Vector-based vaccine.
Effectiveness: 72.0% in the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19.
85% in the prevention of severe COVID-19.
Does not contain egg, latex, or preservatives./strong>
How many doses are needed?
Only one dose in needed.
Who should or shouldn’t get the vaccine?
People who should receive the vaccine are those over 18 years old.
People who should not receive the vaccine are those who have a history of anaphylactic shock (severe allergy) or who are allergic to any component of this vaccine.
What are the possible side effects of the vaccine?
Pain where the injection was given, headache, fatigue, muscle pain, chills, fever, and nausea.
How long will it take for me to be protected and what does it protect me from?
After 28 days of having the complete scheme (the last dose applied), the protection period is still under study. It protects us from 85% serious COVID-19 or requiring hospitalization.
AstraZeneca
and
Oxford
University
AstraZeneca and Oxford University
What is its effectiveness and what does it refer to?
Adenovirus vector-based vaccine.
Effectiveness: 82% after the second dose in the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19.
How many doses are needed?
Two doses are needed, at least 56 days apart (or up to 84 days apart, if necessary).
Who should or shouldn’t get the vaccine?
People who should receive the vaccine are those over 18 years old.
People who should not receive the vaccine are those who have a history of anaphylactic shock (severe allergy) or who are allergic to any component of this vaccine.
What are the possible side effects of the vaccine?
Pain where the injection was given, fatigue, headache, myalgia, arthralgia, and fever, which were mild to moderate in intensity and disappeared within 48 hours of vaccination.
How long will it take for me to be protected and what does it protect me from?
After 14 days of having the complete scheme (after the administration of the 2nd dose), the protection period is still under study. It protects us from serious COVID-19 or requiring hospitalization.
Sputnik V
What is its effectiveness and what does it refer to?
Adenovirus vector-based vaccine.
Effectiveness: 92% after the second dose in the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19.
How many doses are needed?
Two doses are needed, at least 21 days apart (or up to six weeks apart, if necessary).
Who should or shouldn’t get the vaccine?
People who should receive the vaccine are those over 18 years old.
People who should not receive the vaccine are those who have a history of anaphylactic shock (severe allergy) or who are allergic to any component of this vaccine.
What are the possible side effects of the vaccine?
Pain where the injection was given, fatigue, headache, myalgia, arthralgia, and fever, which were mild to moderate in intensity and disappeared within 48 hours of vaccination.
How long will it take for me to be protected and what does it protect me from?
After 14 days of having the complete scheme (after the administration of the 2nd dose), the protection period is still under study. It protects us from serious COVID-19 or requiring hospitalization.
Anti-Herpes Zoster
Herpes zoster is a painful, burning rash. It usually appears on one part of the body and can last for several weeks. It can cause long-lasting severe pain and scarring. Bacterial skin infections, weakness, muscle paralysis, hearing or vision loss may occur less frequently. Herpes zoster is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. After you have had chickenpox, the virus that caused it remains in the body of nerve cells. Sometimes after many years, the virus becomes active again and causes herpes zoster.
Vaccination is indicated in the following cases:
- Immunization of patients from 50 years of age for the prevention of herpes zoster and post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), reduce pain associated with acute or chronic herpes zoster.
Scheme type:
- Single dose.
Rabies
Human rabies is a viral disease transmitted by the bite of an infected animal. It is characterized by acute encephalomyelitis (an aggressive response of the immune system that destroys the myelin layer of the nerves and alters its function at the level of the brain or spinal cord).
Vaccination is indicated in the following cases:
- Prevention of rabies in subjects exposed to risk of contamination. It is recommended for certain international travelers, based on the occurrence of animal rabies in the destination country.
Scheme type:
There are two types.
1. Pre-exposure scheme, consists of three doses of rabies vaccine:
- First dose, on the chosen date.
- Second dose 7 days after the first dose.
- Third dose 28 days after the first dose.
2. Post-exposure scheme, people not vaccinated against rabies, consists of five doses of rabies vaccine.
- First dose, on the date indicated.
- Second dose 3 days after the first dose.
- Third dose 7 days after the first dose.
- Fourth dose 14 days after the first dose.
- Fifth dose 28 days after the first dose.
* If the individual continues to be at risk of exposure to the disease, revaccination should be considered.
Pneumococcal vaccines
Pneumococcal disease can cause serious infections in the lungs (pneumonia), the bloodstream (bacteremia), and the lining of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis).
Two vaccines help prevent pneumococcal disease:
- Pneumoconjugate 13 (pneumococcal conjugate vaccine)
- Pneumococcal 23 (pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine)
Vaccination is indicated in the following cases:
- Active immunization for the prevention of invasive disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in adults 65 years of age and older.
Scheme type:
- *Two pneumococcal vaccines are recommended for all adults 65 years of age or older.
*One dose of Pneumococcal 13 vaccine should be given first, followed by one dose of Pneumococcal 23 vaccine, depending on your age and health.
