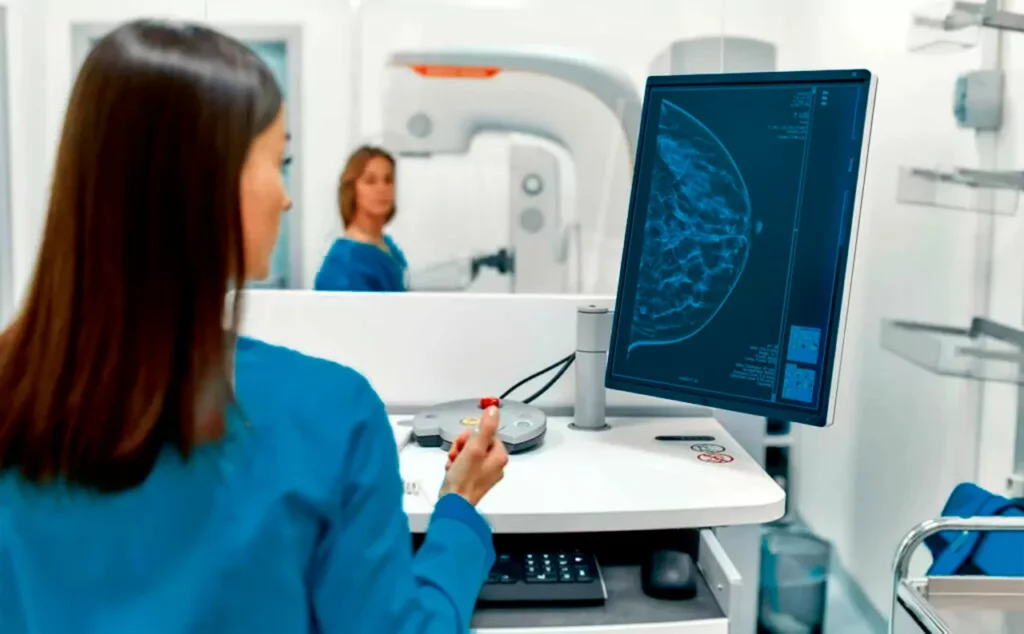
Mammography, also known as a mammogram, is a medical imaging study used to detect the presence of breast cancer in women.
What is a Mammography
A mammography is an X-ray study typically performed annually on women starting at age 40. It may be recommended earlier if there is a family history of breast cancer or specific medical indications that require close monitoring.
This study, different from a breast ultrasound, is designed to detect breast abnormalities at an early stage that could indicate the presence of cancer. It identifies changes or irregularities in breast tissue, as well as the presence of nodules or masses that cannot be felt through physical examination.
How is a Mammography performed
It’s normal for women to have questions before undergoing their first mammography. The procedure involves taking two X-ray images of each breast: one from the side and one from top to bottom.
Once the X-rays are taken, the results will indicate whether the mammography is normal or abnormal.
- Normal mammography: no abnormalities detected, or only benign findings are observed, indicating a 0% chance of breast cancer.
Abnormal mammography: may indicate either benign or malignant findings.
– Benign results can include the presence of lymph nodes, calcifications, or fibroadenomas.
– Malignant results show features that are highly suspicious for breast cancer and must be confirmed through a breast biopsy or additional imaging studies requested by an oncologist.
How a Mammogram Looks When Cancer Is Present
After a mammography is performed, results are reported using a standardized assessment system called BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System), which is divided into seven categories:
- Category 0: the X-ray is inconclusive; additional imaging is needed for evaluation.
- Category 1: no malignancy, lymph nodes, or calcifications, considered a normal mammography.
- Category 2: benign findings, such as normal lymph nodes.
Category 3: probably benign findings, but follow-up is needed within six months.
- Category 4: suspicious findings requiring a confirmatory biopsy.
- Category 5: high suspicion of malignancy and high likelihood of cancer, biopsy required.
- Category 6: malignancy confirmed through a biopsy.
At the ABC Medical Center Women’s Center, we can provide you with specialized care and support. Contact us for more information!
Fuentes:
IMSS, CDC, MedlinePlus