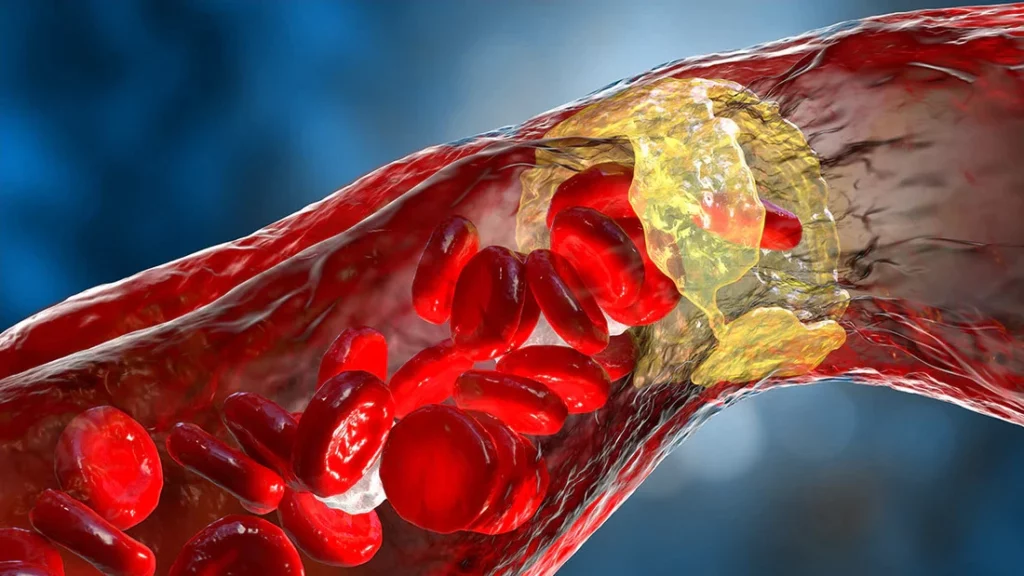
Dyslipidemia is a medical condition involving an imbalance in blood lipid levels, including cholesterol and triglycerides, a situation that can increase the risk of developing serious cardiovascular diseases.
What Is Dyslipidemia?
The term dyslipidemia refers to the presence of abnormal levels of lipoproteins or fats in the blood. These lipoproteins, which transport lipids through the bloodstream, are primarily classified as cholesterol and triglycerides. When present at appropriate levels, they are essential for proper cellular and metabolic function. However, when these levels fall outside the normal range, they can have harmful effects on health.
In general terms, desirable total cholesterol levels should be less than 200 mg/dL*, LDL or bad cholesterol should be below 100 mg/dL, and triglycerides should be less than 150 mg/dL.
On the other hand, HDL or good cholesterol should be above 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women; however, if these values are altered, dyslipidemia can be diagnosed.
Dyslipidemia can be classified based on which lipids are altered and how:
- Hypercholesterolemia: high LDL cholesterol
- Hypertriglyceridemia: high triglycerides
- Hypocholesterolemia: low HDL cholesterol
While genetic inheritance is a common cause—known as familial dyslipidemia—other risk factors include diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and conditions such as diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Síntomas de colesterol y triglicéridos altos
Dyslipidemia is often asymptomatic, which makes it potentially dangerous. However, uncontrolled dyslipidemia may lead to symptoms that become more noticeable once blood vessels have been damaged.
These may include:
- Xanthomas: cholesterol deposits that appear as yellowish bumps on the skin or tendons, often near the elbows, knees, or eyelids
- Xanthelasmas: yellow plaques on the skin, especially around the eyes
- Chest pain: caused by cholesterol buildup in coronary arteries (atherosclerosis)
- Fatigue: due to reduced physical capacity from cardiovascular strain
- Breathing problems, dizziness, or fainting: from restricted blood flow to the brain
It is important to note that high cholesterol and triglycerides usually don’t cause immediate symptoms, which is why regular check-ups are recommended to detect abnormalities before complications arise.
Dyslipidemia can lead to several cardiovascular conditions, such as:
- Atherosclerosis: buildup of plaque in arteries, reducing blood flow and vessel flexibility
- Coronary artery disease: a major risk factor leading to angina and increased risk of heart attack
- Stroke (ischemic event): due to clots or plaque in arteries supplying the brain
- Peripheral artery disease: plaque buildup in leg arteries causes pain, weakness, and walking difficulties
- Hypertension: increased blood pressure caused by stress on arteries and heart, increasing the risk of heart failure
Dyslipidemia Treatment
In dyslipidemia, treatment focuses on reducing abnormal levels of both cholesterol and triglycerides, with the aim of preventing cardiovascular complications. In this regard, the therapeutic approach is based on a comprehensive plan that includes lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication support.
Adopting a healthy diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol is essential, while increasing the intake of fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
Regular exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week to lower triglycerides and raise HDL cholesterol
Weight loss: Even a modest weight reduction can positively affect lipid levels
Limit alcohol and quit smoking: Both contribute to worsening dyslipidemia, and addressing them offers broader health benefits
If medication is required, your doctor may prescribe drugs tailored to your needs—some reduce LDL, others lower triglycerides, some block cholesterol absorption in the intestines, and others help raise HDL levels. Only a specialist can determine the most appropriate medication.
Ongoing monitoring is essential, as dyslipidemia is a chronic condition that may require long-term treatment adjustments.
*mg/dL = milligrams per deciliter
At the Cardiovascular Center, we can help manage the cardiovascular complications of dyslipidemia and provide comprehensive lipid control.
Contact us! Contact us!
Fuentes:
MSD Manuals, IMSS, Fundación Española del Corazón