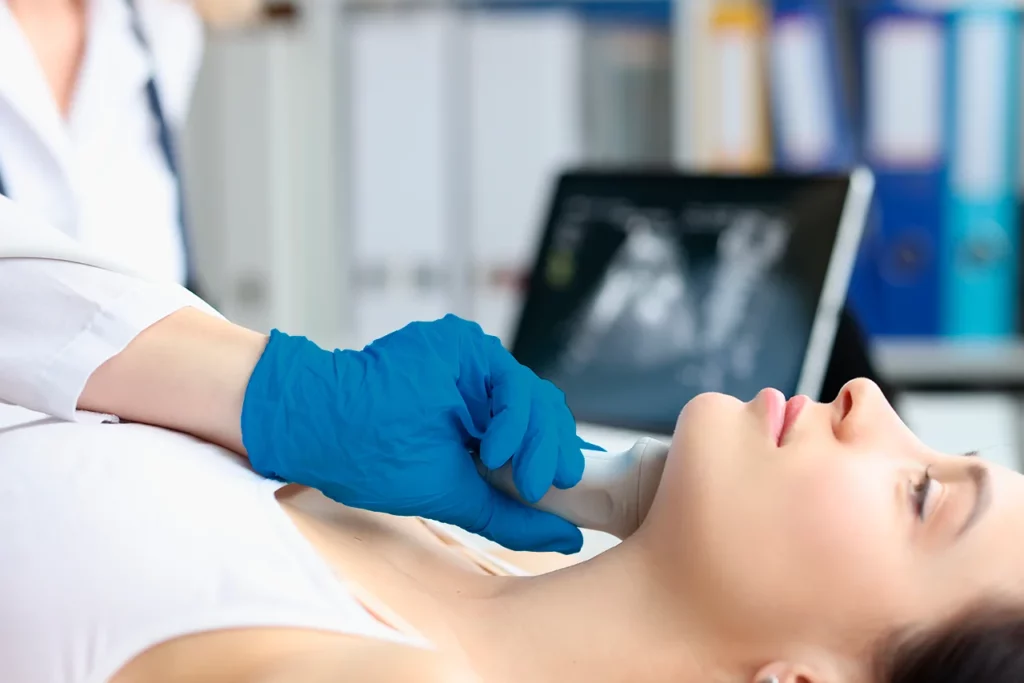
There may be questions about what an ultrasound is and its role in medical examination. This will be addressed in the following article.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a non-invasive medical diagnostic technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to generate images of internal organs, tissues, and other structures.
This technology is based on the principle of echoes, where a device called a transducer emits sound waves that travel through the body and return as echoes when they bounce off internal structures.
Once the echo returns to the transducer, it is converted into images on a screen, allowing physicians to evaluate internal organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues without requiring surgery.
This is why ultrasound is considered a valuable and widely used tool in medicine.
Ultrasound and sonogram are the same
It is common to wonder whether “ultrasound” and “sonogram” refer to the same thing. Depending on the specialist or even the region, the name may vary, but both terms refer to the same diagnostic imaging procedure.
The term sonogram is often used clinically when referring to the study or procedure itself, while ultrasound is more commonly used to refer to the technology or the machine. In conclusion, they describe the same exam.
Types of ultrasound
Ultrasound has evolved to meet different diagnostic needs across medical fields. Some of the most common types include:
- Pelvic ultrasound: used to examine pelvic organs such as the uterus, ovaries, bladder, or prostate; commonly used to evaluate gynecological conditions.
- Obstetric ultrasound or pregnancy ultrasound: one of the best-known applications, used to monitor each trimester of pregnancy and fetal development.
- Structural ultrasound: a specific type used to evaluate the anatomy of organs and tissues in detail; commonly performed during the second trimester of pregnancy to assess fetal development.
- Abdominal ultrasound: helps examine abdominal organs such as the gallbladder, pancreas, liver, kidneys, spleen, and major blood vessels.
- Endovaginal or transvaginal ultrasound: used in gynecology to obtain detailed images of female pelvic organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and cervix.
- Echocardiogram: a specialized heart ultrasound that evaluates the structure and function of the heart; it can be performed in both adults and children (pediatric echocardiography).
- Doppler ultrasound: used to study blood flow in arteries and veins; it measures the change in frequency of sound waves reflected by moving blood.
- Musculoskeletal ultrasound: focused on detecting injuries, tears, ruptures, or other abnormalities in muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints.
- 3D or 4D ultrasound: within ultrasound imaging, there are currently new tools such as 3D ultrasound, which is a three-dimensional ultrasound that allows images of internal structures to be obtained; while 4D ultrasound, in addition to the three-dimensional image, provides movement to the ultrasound.
Ultrasound is an essential tool in modern medicine, allowing physicians to obtain precise information about the condition of internal organs and tissues without invasive procedures.
At ABC Medical Center’s Radiology and Molecular Imaging area, we can provide you with specialized care.
Fuentes:
MedlinePlus, MSD Manuals, Elsevier