What is carotid disease?
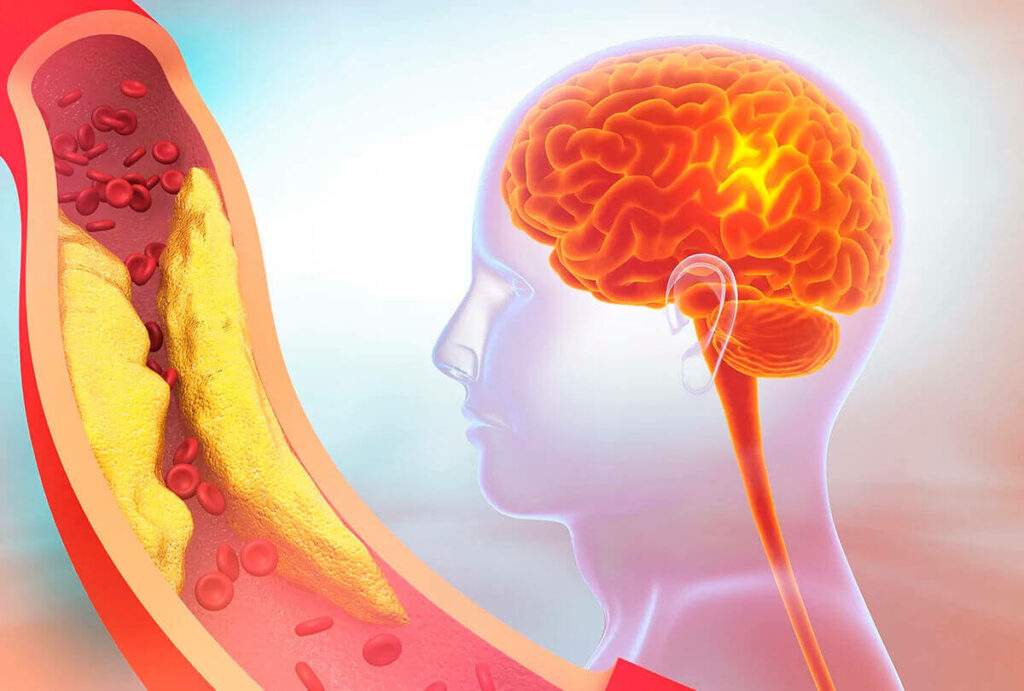
The carotid arteries are the main arteries in the neck that carry circulation and oxygenated blood to the brain.
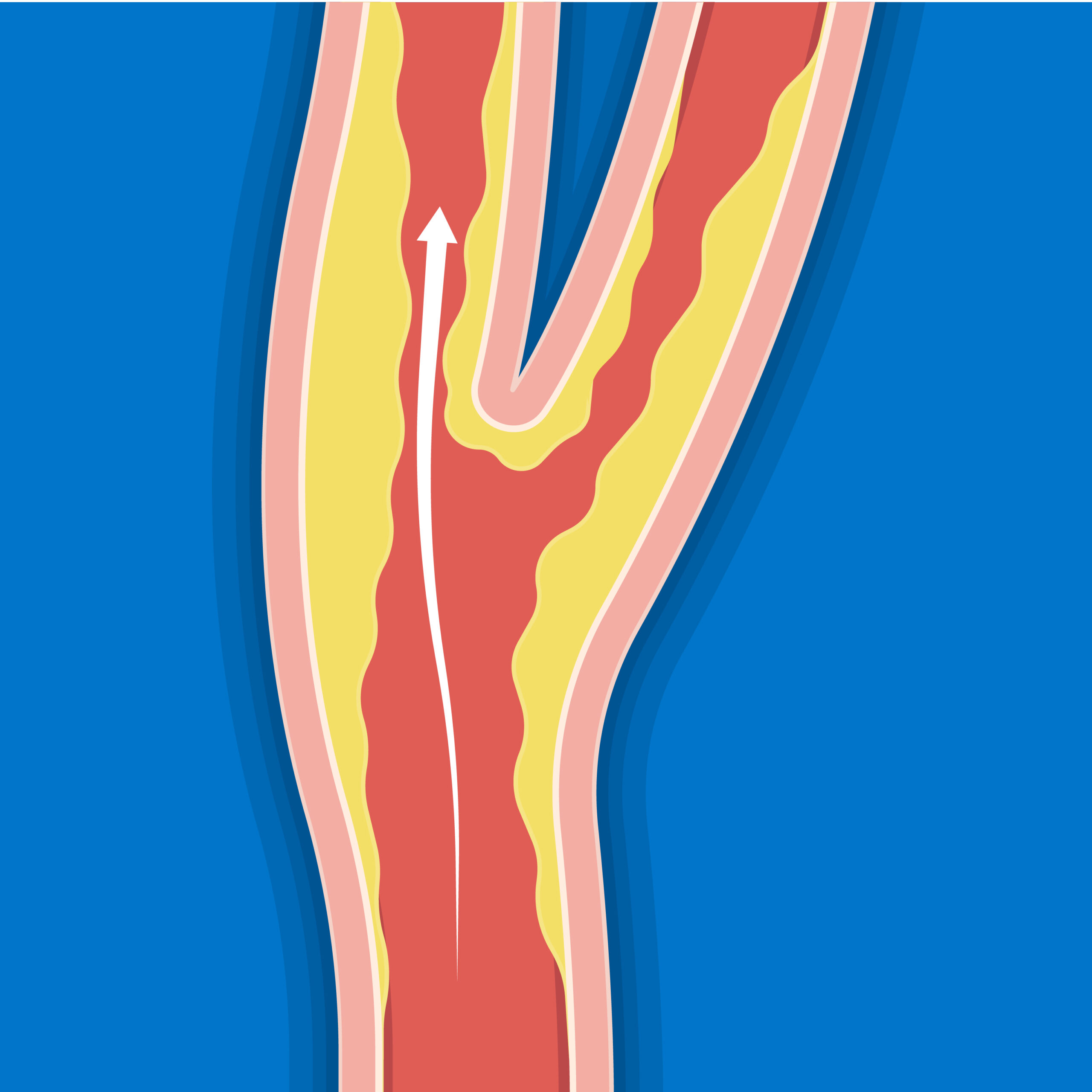
Calcium, cholesterol, and plaques from other substances can build up inside these arteries as you age.
If these plaques block the carotid arteries, small thrombi or fragments of these plaques can break off and travel to the brain causing a minor or major stroke.
About 3% of individuals over the age of 65 have carotid artery disease.
The risk of this disease increases with age and is greater if you have a history of smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or heart disease.
Obstructive carotid artery stenosis is responsible for up to a third of all strokes. In the United States, about 650,000 to 700,000 strokes occur each year, generally in men.
Symptoms of carotid disease
There may be no symptoms even when the obstruction is severe. This condition is usually found on a physical ophthalmologic examination or in the presence of a stroke.
Symptoms such as transient cerebral ischemia can occur in a third of patients with this disease, this can be manifested by weakness of a limb, vision problems, and inappropriate slurred speech.
On some occasions, there may be facial muscle weakness such as deviation of the corner of the lips.
Causes of carotid disease
The most common cause of this disease is the progression of fatty plaques in the carotid arteries, generally due to multiple risk factors such as smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
The diagnosis is performed with a physical examination where a murmur can be heard in the arteries of the neck, or by changes in the retinal arteries.
It is important to see a vascular surgeon who is dedicated to these pathologies and who will request tests such as a carotid duplex, a neck CT angiography, or MR angiography.
Treatment of carotid disease
The treatment of carotid artery disease is focused on reducing the possibility of a stroke.
It specifically depends on the arteries’ degree of obstruction.
Usually, a combination of medications can help slow the progression of carotid artery disease. Aspirin and medications that lower cholesterol and blood pressure are commonly recommended when the disease is lower than 50%.
Quitting smoking is important for managing carotid artery disease and overall health.
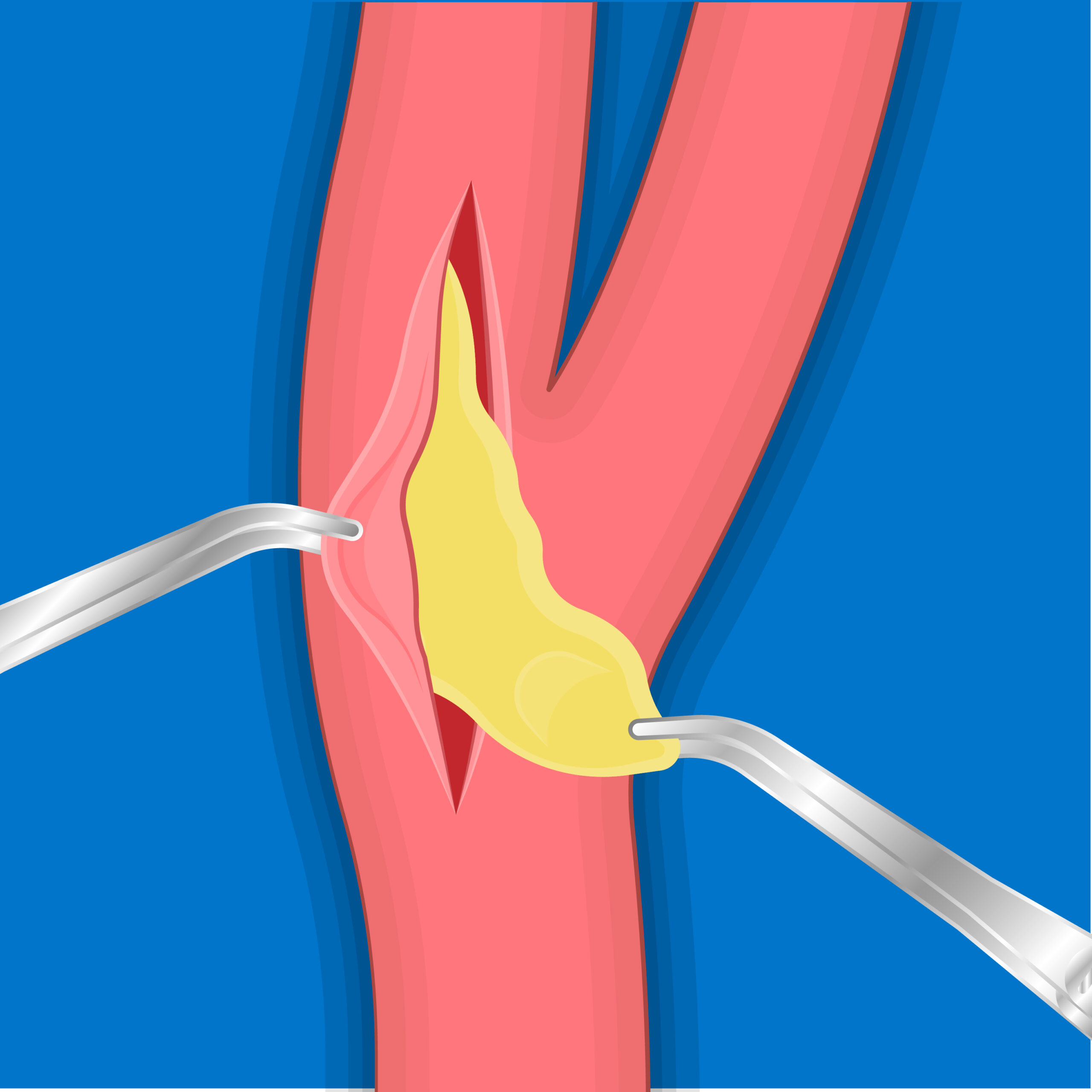
Surgery is recommended if the degree of obstruction is greater than 60%, sometimes open surgery is required, such as carotid endarterectomy, and in some cases with very precise indications, angioplasty with stent placement is required.
At ABC Medical Center’s Cardiovascular Center, we can provide you with specialized care. Contact us!
Fuente: Dr. Salomón Cohen Mussali – Medical specialist in Vascular and Endovascular Surgery of the Medical Center ABC.